Building a Healthy Plate In the hustle and bustle of modern life, maintaining a healthy diet often takes a backseat. However, the significance of what we eat cannot be overstated when it comes to our overall wellness. Building a healthy plate isn’t just about counting calories; it’s about nourishing our bodies with the right balance of nutrients to thrive. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of creating a well-rounded diet that promotes lifelong wellness. Explore More About Health Issues and Their Solutions (How To Improve You Health in 30 Days)
Understanding the Basics of Nutrition 🥦
Before we delve into the specifics of Building a Healthy Plate, it’s essential to understand the basics of nutrition. Our bodies require a variety of nutrients to function optimally, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each nutrient plays a unique role in supporting various bodily functions, from providing energy to supporting immune function and tissue repair.
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Energy Source 🥖
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for our bodies. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels our cells and powers essential functions. Opt for complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which provide sustained energy and essential nutrients.
Proteins: Building Blocks of Life 🍗
Proteins are crucial for Building a Healthy Plate and repairing tissues, as well as supporting immune function and hormone production. Incorporate a variety of protein sources into your diet, including lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Aim for a balanced intake to ensure you’re meeting your body’s needs for essential amino acids.
Fats: Essential for Health 🥑
While fats have earned a bad reputation in the past, they are essential for overall health. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, support brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. Limit saturated and trans fats found in processed and fried foods, as they can increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues.
Vitamins and Minerals: Micronutrients for Vitality 🥕
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients that play a crucial role in numerous physiological processes. They support everything from bone health to immune function and energy production. Ensure you’re consuming a diverse array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to obtain a spectrum of essential vitamins and minerals.

Building Your Plate: The Power of Balance ⚖️
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals of nutrition, let’s explore how to construct a healthy plate that encompasses all essential nutrients. The key lies in balance and variety, as well as mindful portion control.
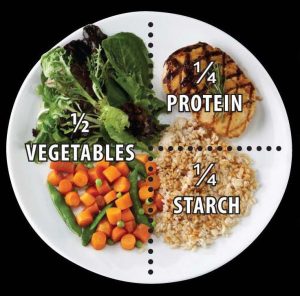
Fill Half Your Plate with Fruits and Vegetables 🍎
Fruits and vegetables are nutritional powerhouses, packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim to fill at least half of your plate with a colorful array of fruits and vegetables, incorporating a mix of leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, berries, citrus fruits, and more. Not only do they provide essential nutrients, but they also add flavor, texture, and visual appeal to your meals.
Include Lean Proteins 🥩
Proteins are essential for muscle repair, satiety, and overall health. Incorporate lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, tofu, tempeh, legumes, and low-fat dairy products into your meals. Opt for grilled, baked, or steamed preparations to minimize added fats and calories.
Choose Whole Grains 🌾
Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an essential component of a healthy diet. Choose whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, barley, oats, and whole wheat bread over refined grains, which have been stripped of their nutritional content. Aim to make at least half of your grain choices whole grains for optimal health benefits.
Don’t Forget Healthy Fats 🥜
Healthy fats play a crucial role in supporting heart health, brain function, and overall well-being. Incorporate sources of healthy fats such as avocado, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish into your meals. Use them in moderation to add flavor and richness to your dishes while reaping their nutritional benefits.
Reduce Sugar 🍭
Limit your intake of added sugars found in processed foods, sugary beverages, and sweets. Excess sugar consumption can contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and various health issues. Opt for naturally sweet foods such as fruits to satisfy your sweet tooth while providing essential nutrients and fiber.
Stay Hydrated 💧
Hydration is essential for overall health and well-being. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support bodily functions. Limit sugary beverages such as soda and fruit juice, opting instead for water, herbal tea, or infused water for added flavor.
Eat from Smaller Plates 🍽️
Choosing smaller plates and bowls can help control portion sizes and prevent overeating. Research suggests that using smaller dinnerware may lead to reduced food intake without feeling deprived. Practice mindful eating and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to determine when you’ve had enough.
Eat Less Red and Processed Meat 🥩
While meat can be a valuable source of protein and essential nutrients, it’s essential to consume it in moderation, particularly red and processed meats. High intake of red and processed meats has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, cancer, and other health issues. Opt for leaner cuts of meat, and incorporate plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, and tofu into your diet for variety and balance.

Additional Tips for Success ✨
In addition to building a healthy plate, there are several other strategies you can implement to support lifelong wellness through diet.
Practice Mindful Eating 🧘♂️
Mindful eating with Building a Healthy Plate involves paying attention to the sensory experience of eating, including taste, texture, and aroma. Slow down and savor each bite, chewing thoroughly and enjoying the flavors of your food. This can help prevent overeating and promote greater satisfaction with meals.
Limit Processed Foods 🚫
Processed foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them less nutritious choices for overall health and Building a Healthy Plate. Limit your intake of processed and packaged foods, opting instead for whole, minimally processed options whenever possible.
Seek Professional Guidance 📋
If you’re unsure about how to create a balanced and nutritious diet, consider seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist. These experts can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs, preferences, and health goals.
Mindful Eating Habits: Enhancing Your Relationship with Food 🍽️
In the realm of nutrition and wellness, the concept of mindful eating habits has gained significant traction. It’s more than just a trend; it’s a holistic approach to nourishing the body and cultivating a healthier relationship with food and Building a Healthy Plate. By incorporating mindfulness into your meals, you can develop a deeper awareness of your body’s hunger and fullness cues, as well as the sensory experience of eating. Here’s a breakdown of mindful eating habits, peppered with delightful emojis to guide you on your journey:
Present Moment Awareness 🧘♂️
Mindful eating and Building a Healthy Plate involves being fully present in the moment while consuming food. Instead of mindlessly devouring your meal, take the time to savor each bite, noticing the flavors, textures, and aromas that tantalize your senses. By bringing your attention to the present moment, you can enhance your enjoyment of food and prevent overeating.
Engage Your Senses 👀👃👅
Engaging all your senses is a fundamental aspect of mindful eating. Take a moment to appreciate the visual appeal of your food, noting its colors, shapes, and presentation. Then, inhale deeply to savor the aroma, allowing it to whet your appetite. As you take your first bite, pay attention to the taste and texture, allowing yourself to fully experience the sensations.
Listen to Your Body 🕰️👂
One of the key principles of mindful eating is tuning into your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Before reaching for seconds or indulging in a snack, pause and check in with yourself. Are you truly hungry, or are you eating out of habit or emotion? Eat slowly and mindfully, stopping when you feel satisfied rather than stuffed. This practice can help prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Practice Gratitude 🙏
Cultivating an attitude of gratitude can enhance your mindful eating experience. Take a moment to express gratitude for the food on your plate, acknowledging the effort and resources that went into its production. By approaching meals with gratitude, you can foster a deeper appreciation for the nourishment they provide and develop a more positive relationship with food.
Minimize Distractions 🚫📱📺
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s easy to multitask while eating, whether it’s scrolling through your phone or watching television. However, distractions can detract from the mindful eating experience, leading to overeating and decreased satisfaction. Instead, create a calm and peaceful environment for meals, free from distractions, allowing yourself to fully focus on the act of eating.
Practice Moderation ⚖️🍪
Mindful eating and Building a Healthy Plate is not about deprivation or strict rules; it’s about finding balance and moderation. Allow yourself to enjoy your favorite foods in moderation, savoring each indulgence without guilt or judgment. By honoring your cravings and practicing moderation, you can maintain a healthy and sustainable approach to eating.
| Aspect | Healthy Plate | Unhealthy Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Half of the plate consists of colorful fruits and vegetables, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. | Minimal or no fruits and vegetables, lacking important nutrients and fiber. |
| Proteins | Lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, tofu, or legumes are included in moderate portions. | High-fat and processed meats dominate the plate, contributing excess saturated fats and sodium. |
| Grains | Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat bread provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals. | Refined grains like white rice or white bread offer little nutritional value and may spike blood sugar levels. |
| Fats | Healthy fats from sources like avocado, nuts, and olive oil are incorporated in moderation. | Unhealthy fats from fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty meats are prevalent, contributing to heart disease risk. |
| Sugar | Limited added sugars, with sweetness coming from natural sources like fruits. | High levels of added sugars from sugary beverages, desserts, and processed foods contribute to weight gain and health issues. |
| Portion Size | Portions are controlled and balanced, promoting satiety without overeating. | Portions are often oversized, leading to excess calorie intake and weight gain. |
Final Thoughts🌟
Building a Healthy Plate is the cornerstone of lifelong wellness. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your meals and practicing portion control, you can nourish your body, support optimal health, and thrive at every stage of life. Remember to focus on balance, variety, and moderation, and prioritize whole, minimally processed foods for maximum nutritional benefit.
FAQS
- Why is it important to fill half of my plate with fruits and vegetables?
- Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and well-being. By incorporating a variety of colorful produce into your meals Building a Healthy Plate, you can ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients to support optimal health.
- What are some examples of lean protein sources?
- Lean protein sources include skinless poultry, fish, tofu, tempeh, legumes, and low-fat dairy products. These foods provide essential amino acids for muscle repair, satiety, and overall health without excess saturated fat and calories.
- Why should I choose whole grains over refined grains?
- Whole grains are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, whereas refined grains have been stripped of their nutritional content during processing. Choosing whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread can help support digestive health, regulate blood sugar levels, and provide sustained energy.
- What are healthy fats, and why are they important?
- Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, play a crucial role in supporting heart health, brain function, and nutrient absorption. These fats provide essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own and should be included as part of a balanced diet.
- How can I reduce my sugar intake?
- Limiting your intake of added sugars found in processed foods, sugary beverages, and sweets can help reduce your overall sugar consumption. Opt for naturally sweet foods such as fruits to satisfy your sweet tooth while providing essential nutrients and fiber.
- What are some tips for staying hydrated?
- Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential for staying hydrated and supporting bodily functions. Limit sugary beverages such as soda and fruit juice, and opt instead for water, herbal tea, or infused water for added flavor.
- Why should I eat from smaller plates?
- Eating from smaller plates can help control portion sizes and prevent overeating. Research suggests that using smaller dinnerware may lead to reduced food intake without feeling deprived, making it a simple yet effective strategy for managing portion sizes.
- Why is it important to limit red and processed meat intake?
- High intake of red and processed meats has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, cancer, and other health issues. Opting for leaner cuts of meat and incorporating plant-based protein sources into your diet can help reduce your risk and promote overall health.
- What is mindful eating, and how can it benefit me?
- Mindful eating and Building a Healthy Plate involves paying attention to the sensory experience of eating, including taste, texture, and aroma. By slowing down and savoring each bite, you can prevent overeating, enhance satisfaction with meals, and develop a healthier relationship with food.
- When should I seek professional guidance for my diet?
- If you’re unsure about how to create a balanced and nutritious diet, consider seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist. These experts can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs, preferences, and health goals.