Introduction
The human body is a marvel of complexity, and the kidneys stand as one of its most vital organs. These bean-shaped powerhouses perform a multitude of essential functions, from filtering waste and toxins to regulating blood pressure and producing hormones. Understanding the science behind healthy kidneys is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate workings of these remarkable organs.
Anatomy and Function
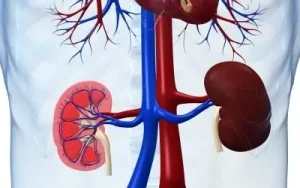
Kidneys, positioned on either side of the spine below the rib cage, are composed of millions of nephrons, the functional units responsible for filtering blood. Their primary role involves filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood, creating urine which is then transported to the bladder. Beyond waste removal, kidneys also play a pivotal role in regulating electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and phosphate, ensuring a delicate balance critical for bodily functions. Additionally, they produce hormones like erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production, and renin, crucial for regulating blood pressure.
Maintaining Kidney Health
Hydration: Adequate water intake is essential for kidney health. It helps flush out toxins and supports proper functioning.
Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins benefits kidney health. Limiting salt, sugar, and processed foods can also reduce the risk of kidney-related issues.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity aids in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and overall well-being, indirectly benefiting kidney health.
Avoiding Toxins: Limiting exposure to harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol helps preserve kidney function.
Common Kidney Conditions
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): This condition involves the gradual loss of kidney function over time. Causes include diabetes, high blood pressure, and other chronic conditions.
Kidney Stones: Formed from crystals in urine, kidney stones can cause excruciating pain and may require medical intervention for removal.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections in the urinary system, if left untreated, can lead to kidney infections and complications.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatment
Medical professionals employ various tests to diagnose kidney-related issues, including blood tests, urine tests, imaging studies like ultrasounds or CT scans, and kidney biopsies. Treatment varies depending on the condition but can include medication, lifestyle changes, dialysis, or in severe cases, kidney transplantation.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy kidneys is integral to overall health. Understanding the science behind their function and adopting healthy lifestyle habits significantly contributes to their well-being. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, hydration, and avoiding harmful substances are key to preventing kidney-related problems. By comprehending the intricate mechanisms and implementing preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their kidney health and enjoy a fulfilling, healthy life. As complex as they are, kidneys are marvels of biological engineering, and their care and maintenance can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Remember, a little awareness and conscientious effort can go a long way in ensuring these vital organs continue to function optimally.