
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity today. As global temperatures rise, weather patterns shift, and extreme events become more frequent, the need for effective solutions becomes increasingly urgent. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool in addressing climate change, offering innovative ways to mitigate its effects. This article explores the multifaceted role of AI in climate change mitigation, highlighting key applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions.
Understanding AI in Climate Change Mitigation
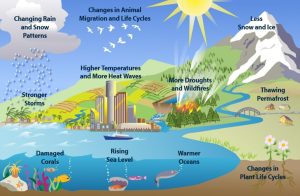
AI, encompassing machine learning, neural networks, and data analytics, refers to systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. In the context of climate change mitigation, AI is employed to analyze large datasets, optimize processes, and develop predictive models. These capabilities are harnessed to enhance our understanding of climate dynamics, improve decision-making, and implement more effective mitigation strategies.
-
Predictive Modeling and Data Analysis
AI algorithms are instrumental in predicting climate patterns and assessing potential impacts. By analyzing vast amounts of historical and real-time data, AI models can forecast future climate conditions, identify trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of different mitigation strategies. For example, machine learning techniques are used to predict extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heatwaves, allowing for better preparedness and response.
-
Energy Efficiency and Optimization
In the energy sector, AI plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and reducing emissions. Smart grids powered by AI optimize the distribution of energy based on demand and supply forecasts, minimizing waste and reducing carbon footprints. AI algorithms are also employed in managing renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, to maximize their efficiency and integration into the grid.
-
Sustainable Agriculture
AI-driven technologies are transforming agriculture by optimizing resource use and reducing environmental impacts. Precision farming, powered by AI, involves using data from sensors, satellites, and drones to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This information helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to more sustainable and less resource-intensive practices.
-
Climate Change Research
AI accelerates climate change research by processing and analyzing complex climate models and simulations. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and correlations within large datasets, aiding scientists in understanding the underlying mechanisms of climate change. This research informs policy decisions and helps develop targeted mitigation strategies.
-
Disaster Management and Response
AI enhances disaster management by improving early warning systems and response strategies. AI-powered systems can analyze data from various sources, including satellites and social media, to detect and predict natural disasters. This capability enables timely evacuations, resource allocation, and disaster response, reducing the impact of extreme weather events.
Benefits of AI in Climate Change Mitigation
The integration of AI into climate change mitigation efforts offers several notable benefits:
- Improved Accuracy and Precision: AI provides highly accurate predictions and analyses, enabling more precise climate modeling and risk assessments.
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI optimizes resource use and operational processes, leading to significant energy savings and reduced emissions.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: AI empowers policymakers and businesses with data-driven insights, facilitating informed decisions and targeted actions.
- Scalability: AI technologies can be scaled and adapted to various sectors and regions, making them versatile tools for global climate action.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, the application of AI in climate change mitigation faces several challenges:
- Data Quality and Availability: AI systems rely on high-quality data for accurate predictions. Incomplete or biased data can lead to unreliable results and hinder effective mitigation efforts.
- Computational Resources: AI models, especially those involving large datasets, require substantial computational power, which can be a barrier for some organizations and regions.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI raises ethical concerns related to privacy, security, and the potential for unintended consequences. Ensuring responsible AI development and deployment is crucial.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Effective climate change mitigation requires collaboration between AI experts, climate scientists, policymakers, and other stakeholders. Coordination across disciplines can be challenging.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. AI-Driven Approaches
To understand the impact of AI on climate change mitigation, it’s useful to compare traditional approaches with AI-driven methods. The following table summarizes key differences:
| Aspect | Traditional Approaches | AI-Driven Approaches |
| Data Analysis | Manual data collection and analysis; limited predictive capabilities. | Automated analysis of large datasets; advanced predictive models. |
| Efficiency | Static systems with fixed optimization; less flexibility. | Dynamic systems with real-time optimization; improved efficiency. |
| Resource Management | Basic resource management techniques; limited integration of renewable sources. | Advanced optimization of resources; enhanced integration of renewable energy. |
| Disaster Response | Reactive approaches; slower response times. | Proactive and predictive approaches; faster and more effective responses. |
| Research and Modeling | Limited by computational power and manual processing. | High-performance computing; detailed and complex climate models. |
Future Directions
The future of AI in climate change mitigation holds promising possibilities. Key areas for future development include:
- Enhanced AI Algorithms: Continued advancements in AI algorithms will improve accuracy, efficiency, and scalability, leading to more effective climate solutions.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Combining AI with other technologies, such as blockchain and IoT, can further enhance climate change mitigation efforts.
- Global Collaboration: Strengthening international collaboration and knowledge sharing will facilitate the development and deployment of AI solutions across different regions and sectors.
- Ethical and Regulatory Frameworks: Developing robust ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks will ensure responsible AI use and address potential risks.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to revolutionize climate change mitigation by providing advanced tools for prediction, optimization, and decision-making. While there are challenges and limitations, the benefits of AI in enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability are substantial. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly crucial role in addressing the complex and urgent challenge of climate change. Collaborative efforts and responsible development will be key to harnessing the full potential of AI in creating a more sustainable future.










