Nuclear Physics delves into the study of atomic nuclei and their interactions. At its core, it explores the fundamental forces that govern the universe at the smallest scales. This branch of science plays a pivotal role in various fields, ranging from energy production to medical diagnostics.
Fundamental Concepts of Nuclear Physics
Atomic Structure and Nucleus
Atoms consist of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, bound together by powerful forces.
Forces Within the Nucleus
The strong nuclear force binds protons and neutrons together, overcoming the electromagnetic repulsion between positively charged protons.
Nuclear Reactions
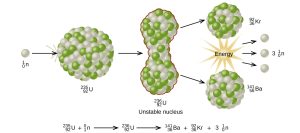
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear fission involves the splitting of heavy atomic nuclei, releasing vast amounts of energy. Fusion, on the other hand, combines light nuclei to form heavier ones, generating even greater energy.
Energy Release and Implications
The energy released in nuclear reactions powers reactors and fuels the sun, offering immense potential for clean and sustainable energy.
Radioactivity
Types of Radioactive Decay
Radioactive isotopes decay through alpha, beta, or gamma emission, transforming into more stable forms.
Decay Processes and Half-life
The half-life of a radioactive substance determines the rate at which it decays, influencing its applications in various fields.
Nuclear Energy Production
Power Plants and Reactors
Nuclear power plants harness the energy released from nuclear reactions to generate electricity, providing a reliable source of low-carbon energy.
Safety Measures and Concerns
Stringent safety protocols are in place to prevent accidents and mitigate the risks associated with nuclear power generation.
Medical Applications
Radiation Therapy
Nuclear physics plays a crucial role in cancer treatment through techniques such as external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Medical imaging technologies like PET and SPECT scans utilize radioactive tracers to visualize internal organs and detect diseases.
Materials Testing
Radiography and neutron activation analysis are used for non-destructive testing of materials in various industries.
Food Irradiation

Nuclear techniques ensure food safety and extend shelf life by eliminating harmful pathogens and pests.
Environmental Impacts
Nuclear Waste Disposal
Efficient disposal methods are essential to manage radioactive waste and minimize environmental contamination.
Contamination and Remediation
Accidental releases of radioactive materials pose environmental challenges, necessitating effective remediation strategies.
Advancements in Nuclear Physics
Research and Discoveries
Ongoing research in nuclear physics leads to breakthroughs in understanding fundamental particles and forces.
Future Prospects
Innovations in nuclear technology hold promise for addressing global challenges such as climate change and energy security.
Ethical Considerations
Nuclear Proliferation
The proliferation of nuclear weapons raises concerns about international security and stability.
International Regulations
Strict regulations and treaties govern the peaceful use of nuclear technology and the prevention of nuclear weapons proliferation.
Public Perception
Common Misconceptions
Public perception of nuclear energy is often influenced by misconceptions and misinformation.
Education and Awareness
Efforts to educate the public about nuclear science and its applications are essential for fostering informed decision-making.
Challenges and Controversies
Nuclear Accidents
Historical nuclear accidents highlight the importance of stringent safety measures and emergency preparedness.
Political Debates
Debates surrounding nuclear energy policy involve considerations of safety, environmental impact, and economic viability.
Role of Nuclear Physics in Space Exploration
Propulsion Technologies
Nuclear propulsion systems enable faster and more efficient space travel, opening up new frontiers in exploration.
Spacecraft Power Sources
Radioisotope thermoelectric generators provide long-lasting power for space missions, even in harsh environments.
Educational Opportunities
Academic Programs
Universities offer specialized programs in nuclear engineering and physics, preparing students for careers in research and industry.
Career Paths in Nuclear Physics
Professionals in nuclear physics contribute to diverse fields, including energy, healthcare, and national security.
Conclusion
Nuclear physics lies at the heart of modern science and technology, offering insights into the fundamental nature of matter and energy. From powering our cities to advancing medical treatments and exploring the cosmos, its impact is profound and far-reaching. As we continue to unlock the mysteries of the atom, the power within nuclear physics will shape the future of humanity.
FAQs
Is nuclear energy safe?
Nuclear energy, when managed properly, is one of the safest forms of energy production with strict safety measures in place.
What are the environmental benefits of nuclear power?
Nuclear power generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, making it a low-carbon energy source.
How do nuclear reactors work?
Nuclear reactors use controlled nuclear reactions to heat water and produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity.
What are the risks of nuclear proliferation?
Nuclear proliferation increases the likelihood of nuclear weapons falling into the wrong hands, posing significant security threats.
How can we address the challenge of nuclear waste disposal?
Research into advanced nuclear fuel cycles and repository technologies is essential for safely managing radioactive waste.










