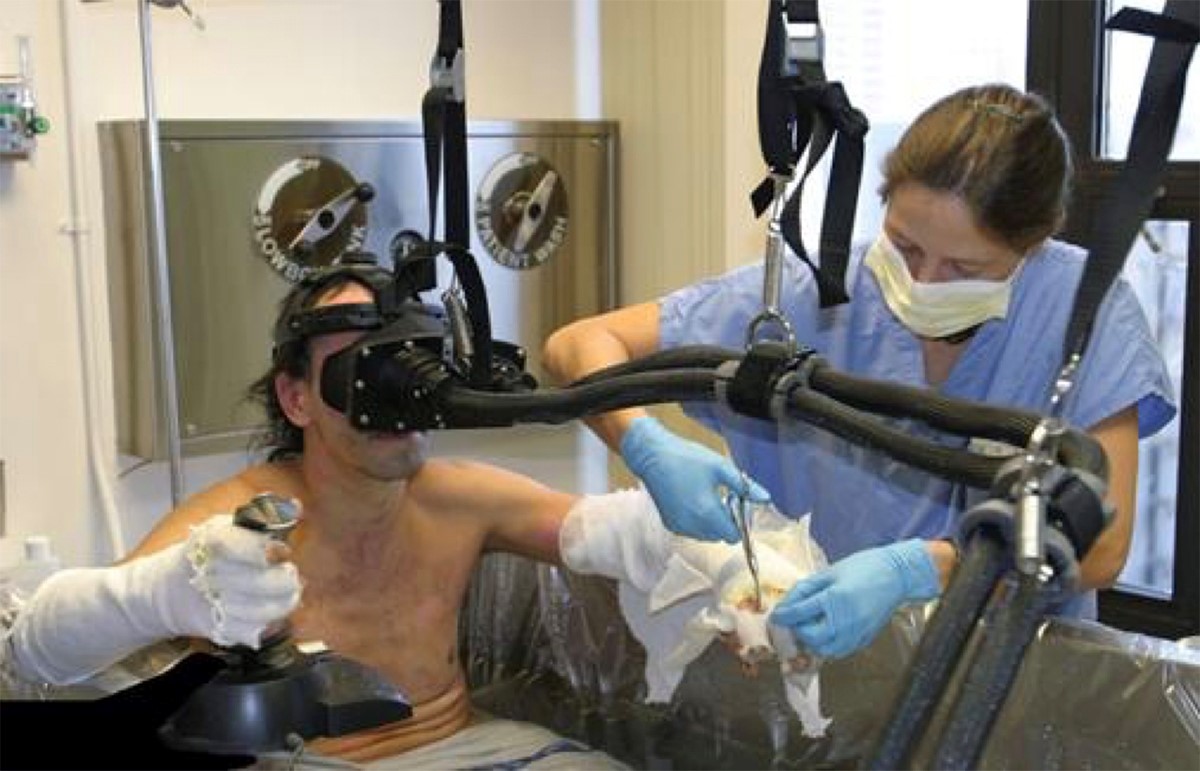
In recent years, the field of pain management has witnessed a revolutionary shift with the advent of Virtual Reality (VR). Once primarily associated with gaming and entertainment, VR has now emerged as a powerful tool in healthcare, offering innovative solutions for pain relief and rehabilitation. This article delves into the rise of VR pain management, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and potential impact on the future of healthcare.
Understanding VR Pain Management
Virtual Reality (VR) pain management involves the use of immersive, computer-generated environments to distract, engage, and ultimately reduce the perception of pain in patients. By leveraging the brain’s natural capacity for sensory processing and distraction, VR can significantly alleviate both acute and chronic pain. The technology typically involves a VR headset that covers the eyes and ears, providing a fully immersive experience that transports patients to a different world, effectively diverting their attention away from the pain.
Mechanisms Behind VR Pain Relief
The effectiveness of VR in pain management can be attributed to several key mechanisms:
- Distraction and Engagement: VR environments are designed to be highly engaging and immersive, capturing the patient’s attention and diverting it away from pain signals. This distraction can lead to a decrease in the perception of pain.
- Sensory Modulation: VR can modulate sensory input by providing alternative sensory experiences. For example, a patient experiencing chronic pain in their leg might be immersed in a VR scenario where they are walking on a beach, feeling the sand and hearing the waves, which can alter their sensory perception and reduce pain.
- Emotional and Cognitive Reframing: VR can also help in reframing the emotional and cognitive aspects of pain. By providing a positive and engaging experience, VR can reduce anxiety, stress, and negative emotions associated with pain, leading to overall pain reduction.
- Neuroplasticity: Repeated VR sessions can promote neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This can help in retraining the brain to process pain signals differently, potentially leading to long-term pain relief.
Applications of VR Pain Management
The applications of VR in pain management are diverse and expanding rapidly. Here are some notable examples:
- Acute Pain Management: VR has shown significant promise in managing acute pain, such as that experienced during medical procedures or post-surgery. For instance, VR can be used to distract patients during wound care, injections, or dental procedures, reducing the need for pharmacological interventions.
- Chronic Pain Management: Chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, and neuropathic pain, can be debilitating and challenging to treat. VR therapy offers a non-invasive and drug-free option for managing chronic pain, providing patients with a sense of control and empowerment over their condition.
- Physical Rehabilitation: VR is increasingly being used in physical rehabilitation to enhance patient engagement and motivation. For example, stroke patients can use VR to simulate real-world activities, aiding in motor skill recovery and reducing pain associated with physical therapy.
- Burn Pain Management: Burn patients often experience intense pain during wound care and physical therapy. VR has been successfully used to distract these patients, significantly reducing their pain levels and improving their overall experience.
- Labor Pain Management: VR is also being explored as a tool for managing labor pain. By immersing expectant mothers in calming and soothing virtual environments, VR can help reduce pain and anxiety during childbirth.
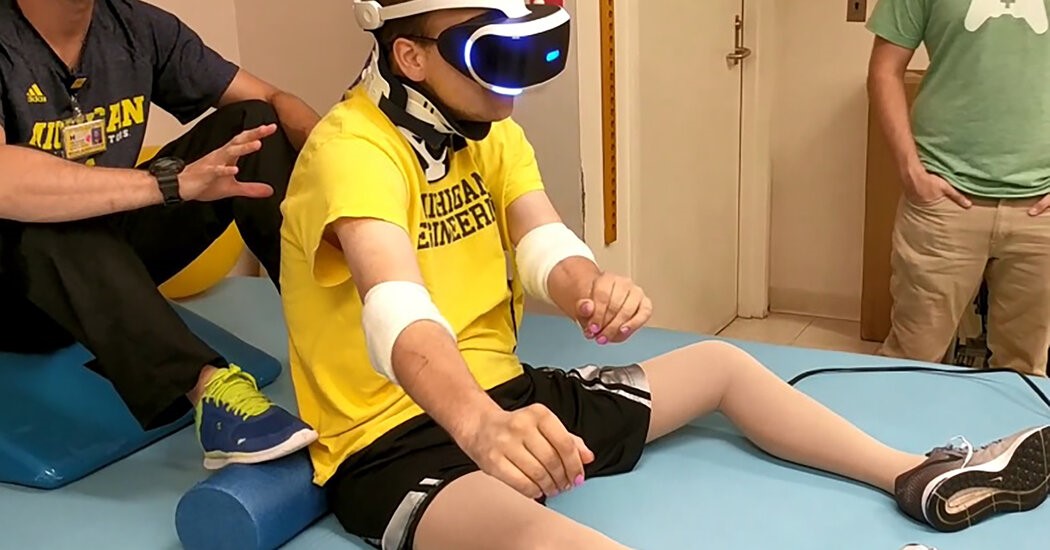
Evidence and Research
The growing body of research on VR pain management provides compelling evidence of its efficacy. Numerous studies have demonstrated the positive impact of VR on pain reduction across various medical contexts. For example, a study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that VR significantly reduced pain intensity and unpleasantness in patients undergoing burn wound care. Another study in the Journal of Medical Internet Research reported that VR therapy led to substantial pain reduction in patients with chronic lower back pain.
Moreover, a meta-analysis published in Pain Medicine reviewed multiple studies and concluded that VR is an effective adjunctive treatment for pain management, particularly for acute pain. These findings underscore the potential of VR as a valuable tool in the pain management arsenal.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of VR pain management is undeniable, there are several challenges and considerations to address:
- Accessibility and Cost: The cost of VR equipment and the need for specialized software can be barriers to widespread adoption. Efforts to develop affordable and user-friendly VR solutions are essential to ensure accessibility for all patients.
- Individual Variability: The effectiveness of VR pain management can vary from person to person. Factors such as age, cognitive function, and the nature of the pain condition can influence the outcomes. Personalized approaches and tailored VR experiences may be necessary to maximize benefits.
- Technical Limitations: VR technology is continually evolving, and there are still technical limitations to overcome. For example, motion sickness and discomfort from prolonged VR use can be issues for some patients. Ongoing research and development are needed to refine and improve VR systems.
- Integration into Clinical Practice: Integrating VR into routine clinical practice requires collaboration between healthcare providers, technologists, and researchers. Training and education for healthcare professionals are crucial to ensure the effective and safe use of VR in pain management.
The Future of VR Pain Management
The future of VR pain management looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and research. As VR systems become more sophisticated and accessible, their applications in pain management are likely to expand further. Here are some potential future developments:
- Personalized VR Therapy: Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning could enable the development of personalized VR experiences tailored to individual patients’ needs and preferences, optimizing pain relief outcomes.
- Remote VR Therapy: Telehealth and remote VR therapy could become more prevalent, allowing patients to access VR pain management from the comfort of their homes. This could be particularly beneficial for individuals with limited mobility or those living in remote areas.
- Integration with Other Therapies: VR could be integrated with other therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness-based interventions, to enhance pain management outcomes. Combining VR with traditional therapies could provide a holistic approach to pain relief.
- Long-term Impact Studies: Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the long-term impact of VR pain management on chronic pain conditions. Understanding the sustained effects of VR therapy will be crucial for its continued integration into clinical practice.
Conclusion
The rise of VR pain management represents a significant advancement in the field of healthcare. By harnessing the power of immersive technology, VR offers a novel and effective approach to pain relief, benefiting patients with both acute and chronic pain conditions. While challenges remain, ongoing research and technological innovations hold the promise of further enhancing the efficacy and accessibility of VR pain management. As we continue to explore and refine this cutting-edge technology, the future of pain management looks brighter than ever.