Introduction
In the realm of sports and recreational activities, head injuries often lurk as underestimated threats. This in-depth exploration seeks to unravel the multifaceted aspects of head injuries, shedding light on various dimensions, from types and causes to symptoms, treatment options, and proactive prevention measures. Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to safeguarding against the potential risks posed by head injuries.
Types of Head Injuries
- Concussion:
- Nature: A prevalent form of traumatic brain injury (TBI).
- Insight: Can occur without a direct impact to the head.
- Contusion:
- Nature: A bruise on the brain leading to bleeding.
- Complications: Potential for swelling and various complications.
- Intracranial Hematoma (ICH):
- Nature: Bleeding beneath the skull forming a clot.
- Severity: Categorized based on location and degree.
- Skull Fracture:
- Nature: Breakage of the skull bone affecting the brain.
- Complications: May cause additional injuries and complications.
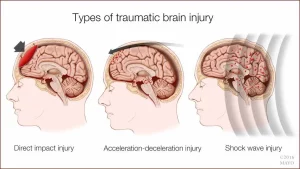
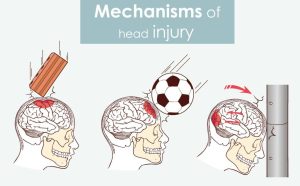
Causes
A nuanced understanding of the root causes of head injuries is paramount:
- Car Accidents: A leading cause with varying severities.
- Falls: Particularly significant in older adults and children.
- Child Abuse: A distressing contributor to severe head trauma.
- Acts of Violence: Can result in profound and lasting head injuries.
- Sports-Related Activities: High-risk sports include cycling, football, basketball, and more.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a head injury is pivotal for prompt and effective intervention:
- Common Signs: Confusion, depression, dizziness.
- Physical Symptoms: Headache, memory loss, nausea.
- Emergency Signs: Convulsions, impaired senses, loss of consciousness.
Treatment
Navigating the treatment landscape involves a comprehensive approach and immediate action:
- Prevent Further Injury:
- Cease activity and seek medical assistance promptly.
- Emphasize the reporting of potential injuries in sports for timely intervention.
- Medical Attention:
- Critical for moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs).
- Rigorous monitoring of symptoms, diagnostic tests, and imaging procedures.
- Severe cases may necessitate surgical intervention to relieve pressure and mitigate complications.
- Rehabilitation:
- In-depth physical and occupational therapy tailored to individual needs.
- Medication, psychological counseling, and robust social support.
- Acknowledging the varied recovery timelines; rehabilitation often extends over a prolonged period.
Risk/Prevention
Proactive steps to mitigate the risk of head injuries encompass various facets:
- Protective Head Gear:
- Utilize gear approved by ASTM for specific activities.
- Highlight the significance of proper fit and usage for enhanced effectiveness.
- Q-Collar Device:
- An FDA-approved noninvasive device offering a potential breakthrough.
- Reduces brain movement, presenting a promising avenue for preventing head injuries.
- Additional Safety Measures:
- Incorporate light-reflecting clothing for nighttime activities.
- Adhere strictly to safety rules at water parks and swimming pools.
- Vigilant supervision and education on proper sports equipment use, particularly for children.
Conclusion
This extensive exploration delves deep into the multifaceted realm of head injuries, aiming to empower individuals with comprehensive knowledge. By prioritizing safety, incorporating protective gear, and recognizing emergency signs, individuals can navigate various activities with heightened awareness and reduced risk. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your safety in the intricate landscape of head injuries.