In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern medicine, technology is playing an increasingly vital role in transforming emergency healthcare services. The integration of cutting-edge technologies is not only enhancing the speed and efficiency of emergency responses but also improving patient outcomes and overall healthcare delivery. This article delves into the various ways technology is revolutionizing emergency healthcare services, highlighting key innovations and their impact on the field.
The Role of Technology in Emergency Healthcare
Emergency healthcare services are designed to provide immediate medical attention to individuals experiencing acute medical conditions, trauma, or other life-threatening situations. The primary objective is to stabilize patients and ensure they receive the necessary care as swiftly as possible. Over the years, technological advancements have significantly improved the ability of emergency healthcare providers to achieve this goal. Here are some of the most notable technological innovations transforming emergency healthcare:
1. Telemedicine and Telehealth
Telemedicine has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of emergency healthcare. Through the use of video conferencing, remote monitoring, and other telecommunication technologies, healthcare providers can offer timely medical consultations and diagnoses to patients in remote or underserved areas. Telehealth platforms enable emergency medical teams to connect with specialists in real-time, ensuring that patients receive expert care even when they are far from a hospital.
For example, in rural areas where access to specialized medical care is limited, telemedicine allows emergency responders to consult with neurologists, cardiologists, and other specialists to make informed decisions about patient care. This can be particularly crucial in cases of stroke, heart attack, or severe trauma, where every second counts.
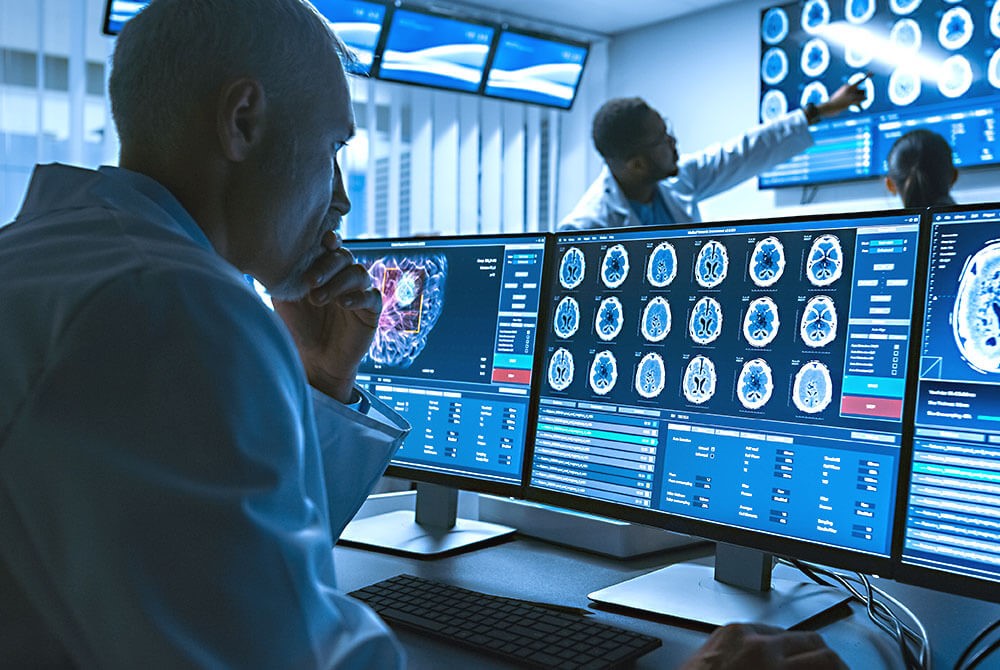
2. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
The advent of portable diagnostic tools has significantly improved the capabilities of emergency healthcare providers. Handheld ultrasound devices, portable X-ray machines, and point-of-care testing kits allow paramedics and emergency room physicians to quickly assess a patient’s condition and make informed treatment decisions on the spot.
For instance, handheld ultrasound devices enable paramedics to perform rapid assessments of internal injuries, such as internal bleeding or organ damage, while still on the scene. This immediate diagnostic capability can guide treatment decisions and prioritize patients for transport to specialized trauma centers.
3. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have revolutionized the way patient information is managed and shared in emergency healthcare settings. EHR systems provide healthcare providers with instant access to a patient’s medical history, allergies, medications, and previous treatments. This comprehensive view of a patient’s medical background is invaluable in emergency situations, where timely and accurate information can make a significant difference in patient outcomes.
Moreover, EHRs facilitate seamless communication and coordination among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the emergency care team are on the same page. This level of coordination is essential for delivering efficient and effective care, especially in high-pressure emergency scenarios.
4. Mobile Health Applications
Mobile health applications, or mHealth apps, are empowering both patients and healthcare providers in emergency situations. These apps offer a range of functionalities, from providing first aid instructions and emergency contact information to enabling real-time communication with emergency medical services (EMS).
For example, some mHealth apps allow users to share their location and medical information with EMS dispatchers, enabling faster and more accurate responses. Additionally, apps that offer first aid guidance can help bystanders provide crucial assistance to individuals in distress before professional help arrives.

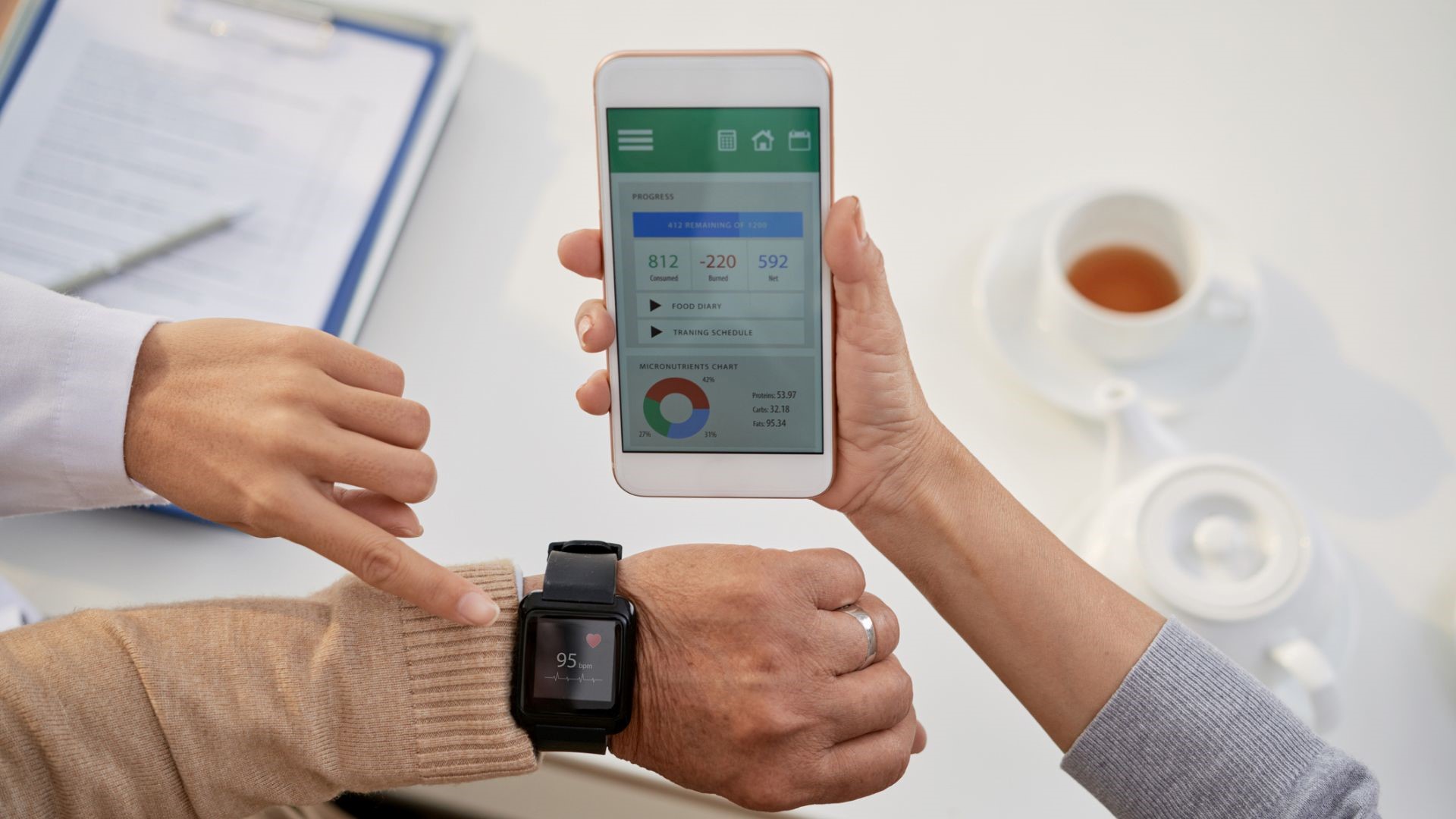
5. Wearable Health Devices
Wearable health devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are becoming increasingly popular tools for monitoring and managing health. These devices can track vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, and alert users to potential health issues. In emergency situations, wearable devices can provide valuable data to healthcare providers, enabling them to make more informed decisions about patient care.
For instance, a smartwatch that detects an irregular heartbeat or a sudden drop in oxygen levels can trigger an alert, prompting the wearer to seek medical attention. In some cases, these devices can even automatically notify emergency services, ensuring a rapid response to potential medical emergencies.
6. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are making significant strides in emergency healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, predicting patient outcomes, and optimizing resource allocation. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent to human clinicians.
For example, AI can assist in the early detection of sepsis, a life-threatening condition that requires prompt treatment. By analyzing patient data, including vital signs and laboratory results, AI algorithms can identify early warning signs of sepsis and alert healthcare providers, allowing for timely intervention.
Moreover, AI-driven predictive analytics can help EMS dispatchers optimize ambulance deployment and route planning, ensuring that emergency responders reach patients as quickly as possible. This can be particularly beneficial in urban areas with high traffic congestion or during large-scale emergencies.
7. Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are emerging as valuable assets in emergency healthcare. These technologies can be used to deliver medical supplies, such as blood, medications, and defibrillators, to remote or inaccessible areas. Additionally, drones equipped with cameras and sensors can provide real-time aerial surveillance of disaster zones, helping emergency responders assess the situation and plan their response.
For example, in cases of natural disasters, such as earthquakes or floods, drones can quickly survey affected areas and identify individuals in need of rescue. This information can be relayed to emergency teams on the ground, enabling them to prioritize their efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
8. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are also making their mark on emergency healthcare services. Robotic systems can assist with various tasks, from performing minimally invasive surgeries to delivering medications and supplies within hospitals. In emergency settings, robots can be deployed to handle hazardous materials or assist in search and rescue operations.
For instance, robotic-assisted surgery can enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision and control, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. In disaster scenarios, robots equipped with sensors and cameras can navigate through debris and locate survivors, providing crucial assistance to human rescuers.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the integration of technology in emergency healthcare services offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges. Ensuring the security and privacy of patient data, addressing interoperability issues between different systems, and managing the costs associated with implementing new technologies are some of the key concerns that need to be addressed.
Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancement requires ongoing training and education for healthcare providers to stay up-to-date with the latest tools and techniques. Ensuring that emergency healthcare professionals are proficient in using new technologies is essential for maximizing their potential and improving patient care.
Looking ahead, the future of emergency healthcare services is likely to be shaped by continued innovations in technology. Advances in AI, robotics, and telemedicine are expected to further enhance the capabilities of emergency responders and healthcare providers. Additionally, the development of new wearable devices and mobile health applications will empower individuals to take a more active role in managing their health and seeking timely medical assistance.
Conclusion
Technology is undeniably transforming emergency healthcare services, offering new possibilities for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the efficiency of emergency responses. From telemedicine and advanced diagnostic tools to AI and robotics, these innovations are revolutionizing the way emergency healthcare is delivered. As technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of emergency healthcare, ultimately saving lives and improving the quality of care for patients in need.