In an era where technology is reshaping every aspect of our lives, the healthcare sector is no exception. Digital health platforms are emerging as transformative tools that are revolutionizing patient care and improving outcomes in ways previously unimaginable. These platforms leverage advanced technologies to offer a range of services, from telemedicine and remote monitoring to data analytics and personalized treatment plans. This article explores how digital health platforms are making a significant impact on patient outcomes.
The Rise of Digital Health Platforms
Digital health platforms encompass a broad spectrum of technologies designed to improve healthcare delivery. They include mobile health apps, telehealth services, wearable devices, and sophisticated data analytics systems. The primary aim of these platforms is to enhance the quality of care, increase accessibility, and reduce costs. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital health platforms, highlighting their importance in modern healthcare.
Enhancing Accessibility and Convenience
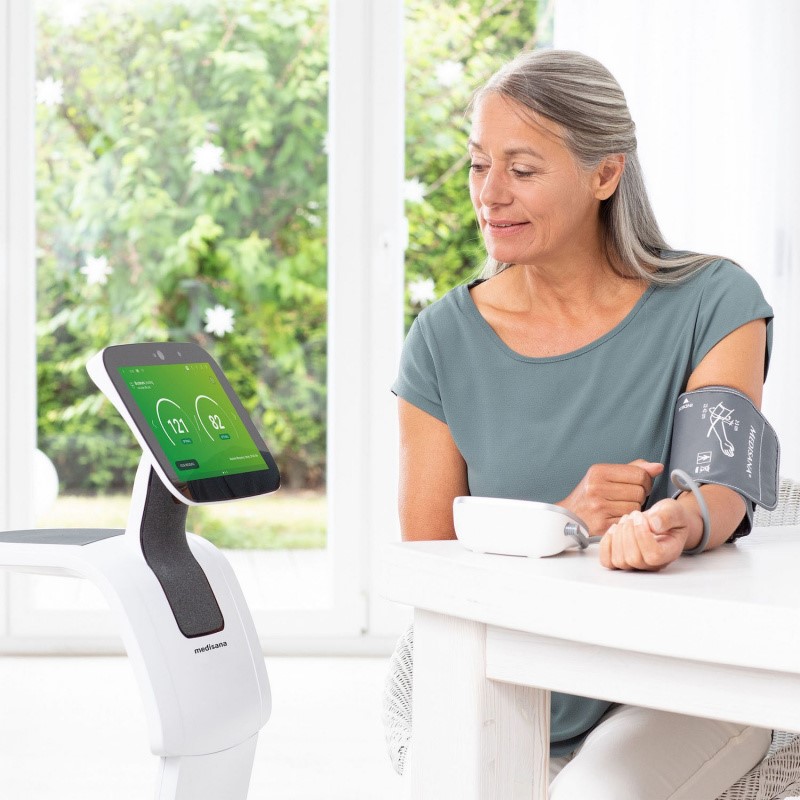
One of the most significant advantages of digital health platforms is their ability to make healthcare more accessible. Telemedicine services, for example, allow patients to consult with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes. This is particularly beneficial for individuals living in remote areas or those with mobility issues. By reducing the need for physical visits, telemedicine also helps in minimizing the risk of infectious diseases, a critical factor during pandemics.
Moreover, digital health platforms offer round-the-clock access to medical advice and support. Patients can schedule appointments, receive reminders, and access their medical records at any time. This level of convenience ensures that patients are more likely to adhere to their treatment plans, leading to better health outcomes.
Personalized Treatment Plans
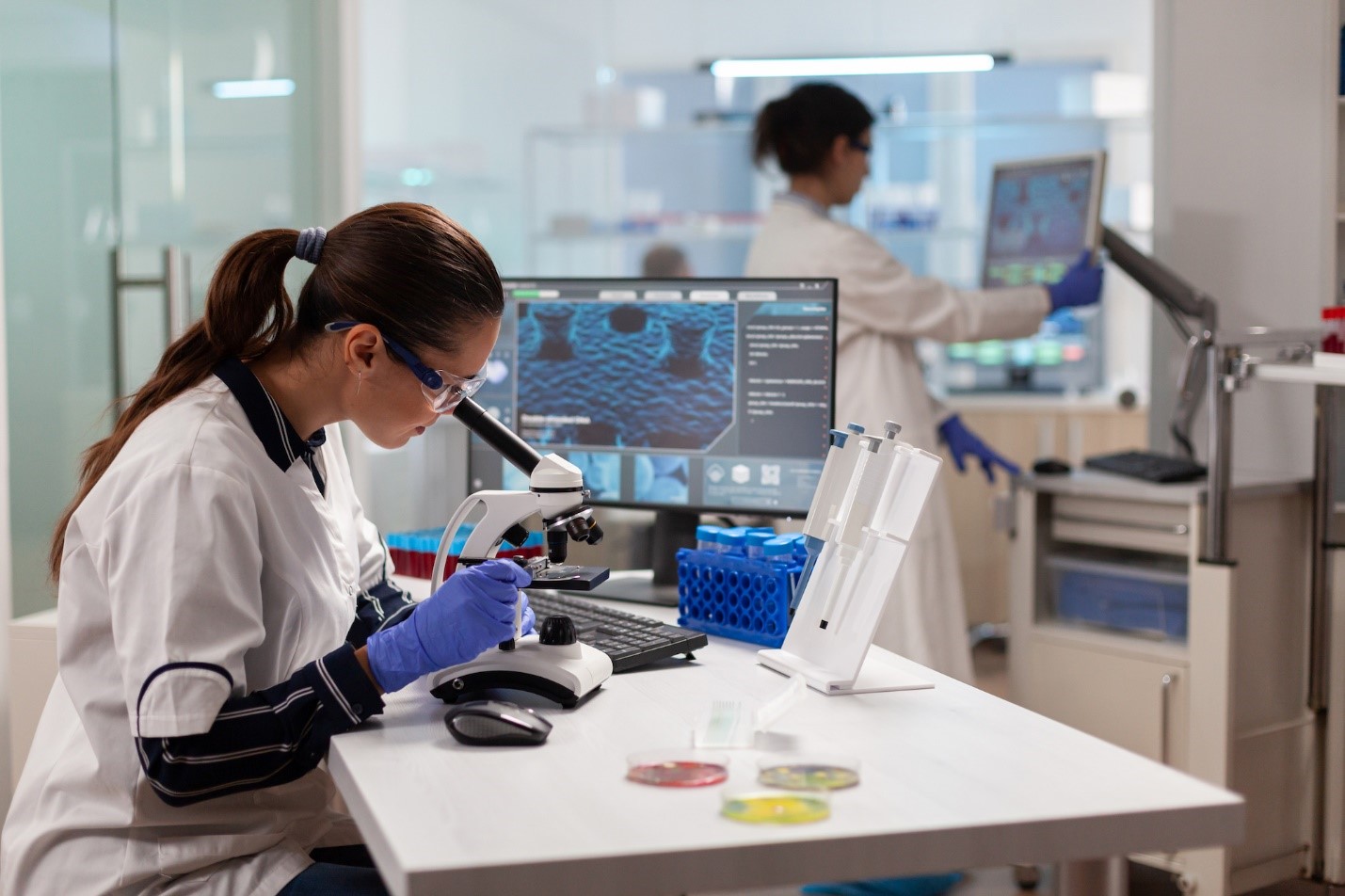
Digital health platforms are adept at collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data. This capability enables healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Wearable devices, for instance, can monitor vital signs, physical activity, and sleep patterns. The data collected can then be analyzed to provide insights into a patient’s health status, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in this process. They can identify patterns and predict health trends, enabling proactive interventions. For example, AI can predict the likelihood of a patient developing a chronic condition based on their lifestyle and genetic factors. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare systems.
Improved Patient Engagement and Empowerment
Digital health platforms empower patients by giving them greater control over their health. Mobile health apps, for example, provide educational resources, medication reminders, and tools for tracking symptoms and progress. These features encourage patients to take an active role in managing their health, leading to increased engagement and better adherence to treatment plans.
Furthermore, digital platforms facilitate seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers. Secure messaging systems and virtual consultations allow for continuous monitoring and support. Patients can easily report any concerns or changes in their condition, enabling timely interventions and reducing the risk of complications.
Enhanced Coordination of Care
Effective coordination of care is essential for managing complex health conditions, especially for patients with multiple chronic diseases. Digital health platforms streamline the sharing of information among healthcare providers, ensuring that everyone involved in a patient’s care is on the same page. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are a prime example of this. They provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, including diagnoses, treatments, and test results.
By facilitating better communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, digital health platforms help in reducing medical errors and improving the overall quality of care. Patients receive more consistent and coherent treatment, which is crucial for achieving positive health outcomes.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Digital health platforms contribute to cost reduction and efficiency in several ways. Telemedicine reduces the need for physical infrastructure and administrative overheads associated with in-person visits. Remote monitoring and wearable devices can detect potential health issues early, preventing costly hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
Data analytics and AI also play a role in optimizing resource allocation. Predictive analytics can forecast patient demand, enabling healthcare providers to better manage their resources and reduce wait times. This not only improves the patient experience but also enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Addressing Challenges and Future Prospects
While digital health platforms offer numerous benefits, they also present certain challenges. Data privacy and security are major concerns, as these platforms handle sensitive patient information. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is essential to protect patient data.
Additionally, the digital divide poses a challenge. Not all patients have access to the necessary technology or the digital literacy to use these platforms effectively. Addressing these disparities is crucial to ensure that the benefits of digital health platforms are accessible to all.
Looking ahead, the future of digital health platforms is promising. Advances in AI, machine learning, and blockchain technology are expected to further enhance the capabilities of these platforms. Integration with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G, will enable even more sophisticated and real-time health monitoring and interventions.
Conclusion
Digital health platforms are playing a pivotal role in transforming healthcare delivery and improving patient outcomes. By enhancing accessibility, personalizing treatment plans, empowering patients, and improving coordination of care, these platforms are addressing some of the most pressing challenges in healthcare. While there are hurdles to overcome, the potential benefits far outweigh the challenges. As technology continues to evolve, digital health platforms will undoubtedly become an integral part of the healthcare landscape, paving the way for a healthier future.