Introduction
Edema, colloquially known as swelling, is a prevalent medical condition that warrants a closer examination. In this in-depth article, we embark on a journey to understand the various facets of edema, including its types, underlying causes, symptoms, and the nuanced approaches to treatment.
Types of Edema
1. Peripheral Edema
Peripheral edema manifests primarily in the legs, feet, and ankles, often signaling potential issues within the circulatory system, lymph nodes, or kidneys. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective management.
2. Pedal Edema
Characterized by fluid accumulation in the feet and lower legs, pedal edema is more prevalent in older individuals or during pregnancy. The impact on mobility necessitates a closer examination of contributing factors.
3. Lymphedema
Affecting the arms and legs, lymphedema is frequently a consequence of damage to lymph nodes, typically induced by cancer treatments. This highlights the intricate relationship between medical interventions and potential side effects.
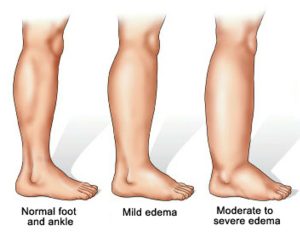
4. Pulmonary Edema
A critical condition where fluid collects in the air sacs of the lungs, resulting in breathing difficulties. Swift medical attention is imperative, with symptoms including a rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and coughing up foamy spittle.
5. Cerebral Edema
An alarming situation involving fluid accumulation in the brain, often triggered by head trauma, vascular issues, tumors, or allergic reactions. Recognizing the severity of cerebral edema is crucial for timely intervention.
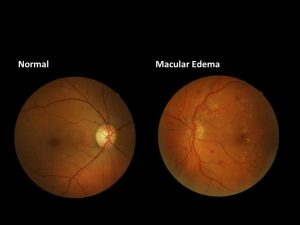
6. Macular Edema
Involving fluid buildup in the macula of the eye, macular edema can impair vision and is frequently associated with damaged blood vessels. Understanding the ocular implications adds another layer to the diverse manifestations of edema.
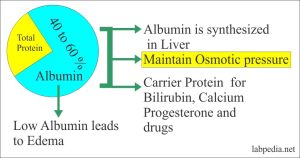
Causes of Edema
Edema can arise from a myriad of factors, ranging from common injuries to underlying medical conditions. Key contributors include:
- Low levels of albumin, impacting fluid retention
- Allergic reactions, leading to vascular leakage
- Obstruction of fluid drainage, causing backup and swelling
- Critical illnesses, prompting widespread fluid leakage
- Congestive heart failure, resulting in leg edema or fluid in the lungs
- Liver disease, causing fluid retention in the abdomen
- Kidney disease, contributing to severe leg edema or generalized swelling
- Pregnancy-related edema, with complications like deep vein thrombosis and preeclampsia
- Medications, including NSAIDs, (Lasix) calcium channel blockers, and corticosteroids, which may induce mild leg edema
Refer to the comparative table for an in-depth exploration of edema causes, aiding in a comprehensive understanding.
Symptoms of Edema
Symptoms of edema are diverse, dependent on the extent and location of swelling. Examples include:
- Localized swelling with minimal or no accompanying symptoms
- Painful swelling in the case of allergic reactions
- Tongue or throat edema, presenting life-threatening implications in food or medicine allergies
- Heavy legs and impaired mobility in cases of leg edema, impacting daily activities
- Shortness of breath and potential low oxygen levels in pulmonary edema, often accompanied by a persistent cough
The distinction between pitting and non-pitting edema provides valuable diagnostic insights for healthcare professionals, aiding in the identification of underlying causes.
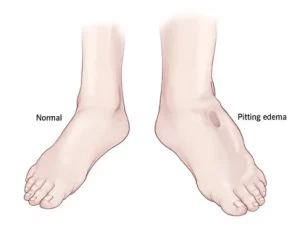
Treatment of Edema
Effectively managing edema necessitates a tailored approach that addresses the root cause. Treatment modalities include:
- Allergy medications to alleviate swelling in response to allergic reactions
- Blood thinners for clot-related edema, restoring normal fluid drainage
- Surgical interventions, chemotherapy, or radiation for tumor-induced edema
- Diuretics and sodium restriction for managing edema associated with heart failure or liver disease
A comprehensive understanding of the underlying cause is paramount for devising an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of edema provides a comprehensive understanding of this prevalent medical condition. From its various types affecting different parts of the body to the diverse causes stemming from injuries, medical conditions, and medications, edema requires careful consideration for effective management.
Recognizing the symptoms, whether localized or systemic, aids in early detection and prompt intervention. The distinction between pitting and non-pitting edema serves as a valuable diagnostic tool for healthcare professionals, guiding them in pinpointing the underlying causes.
Treatment strategies are diverse and tailored to address the root cause of edema. Whether it’s utilizing allergy medications for allergic reactions, administering blood thinners for clot-related edema, or considering surgical interventions for tumor-induced swelling, a personalized approach is crucial.
Individuals experiencing persistent swelling are encouraged to seek consultation with healthcare professionals. A comprehensive evaluation will help determine the appropriate treatment plan, ensuring optimal outcomes and improved quality of life. Stay informed about edema, stay proactive about your health.