The monsoon season brings relief from the scorching heat but also poses health risks, especially concerning brain infections. It’s crucial to understand the potential dangers and take necessary precautions to safeguard our well-being during this time.
1. Understanding the Risks:
During the monsoon, the increased humidity and waterlogging create favorable conditions for the proliferation of disease-causing bacteria and viruses. Brain infections, such as meningitis and encephitis, can occur due to the transmission of pathogens through contaminated water or mosquito bites, posing a significant health threat.
2. Recognizing Symptoms:
Brain infections can manifest in various ways, depending on the type of infection and its severity. Common symptoms include severe headache, fever, confusion, neck stiffness, sensitivity to light, nausea, and vomiting. Prompt recognition of these signs is crucial for early detection and intervention to prevent complications.
3. Meningitis and Encephalitis:
Meningitis is the inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, while encephalitis is the inflammation of the brain. Both conditions can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites, with viral infections being more common during the monsoon season.
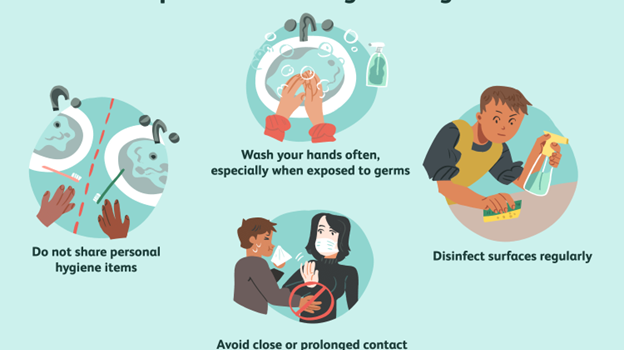
4. Transmission and Prevention:
Brain infections are primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets, contaminated water or food, and insect bites. To reduce the risk of infection, it’s essential to practice good hygiene, avoid stagnant water, use mosquito repellent, and ensure vaccination against preventable diseases like Japanese encephalitis.
5. Precautionary Measures:
Taking preventive measures is crucial to mitigate the risks of brain infections during the monsoon. Maintaining cleanliness, drinking safe and filtered water, avoiding street food, using insect repellents, and wearing protective clothing can help minimize exposure to pathogens and reduce the likelihood of infection.
6. Medical Consultation:
If you experience persistent symptoms such as severe headache, fever, altered consciousness, seizures, or neurological deficits during the monsoon, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in managing brain infections effectively and preventing long-term complications.
7. Hydration and Immune Support:
Staying hydrated and maintaining a strong immune system are essential in protecting against infections. Consuming fresh fruits, vegetables, and immunity-boosting foods rich in vitamins and nutrients can help fortify your body’s defenses and enhance resilience against pathogens during the monsoon.
8. Environmental Precautions:
Be cautious of your surroundings and take necessary precautions to avoid exposure to potential sources of infection. Avoid walking barefoot in waterlogged areas, ensure proper sanitation and waste disposal practices, and stay informed about disease outbreaks in your locality to proactively protect yourself and your family.
9. Public Health Initiatives:
Public health authorities play a critical role in monitoring and controlling infectious diseases during the monsoon. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, following government advisories, and participating in vaccination drives can contribute to community-wide efforts in preventing the spread of brain infections and other health risks associated with the rainy season.

10. Community Awareness and Advocacy:
Raising awareness about the risks of brain infections during the monsoon is essential for promoting community health and safety. Engage in advocacy efforts, educate others about preventive measures, and support initiatives that prioritize public health and well-being to create a more resilient and informed society in the face of health challenges.