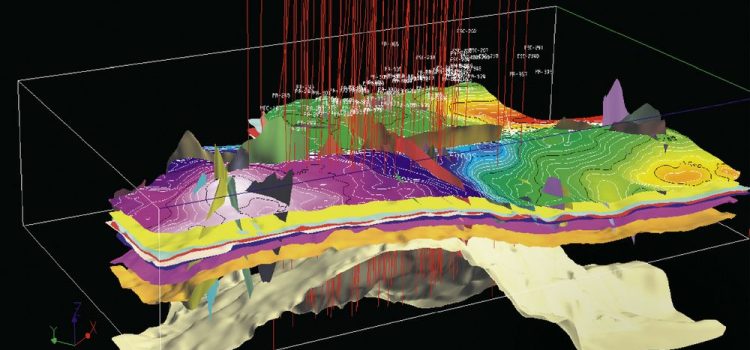
Geophysics is the scientific discipline that explores the physical properties and processes of the Earth’s by utilizing principles of physics and mathematics. It serves as a vital gateway to understanding the intricate structure of our planet, ranging from its surface features to its innermost depths.
Methods Used in Geophysics
Seismic Methods
Seismic methods involve the study of seismic waves generated by natural phenomena or artificial sources. These waves provide crucial information about subsurface structures, such as the composition and density of rock layers.
Gravity Methods
Gravity methods measure variations in the Earth’s gravitational field to map subsurface features like density contrasts and geological structures. By analyzing gravitational anomalies, geophysicists can infer the presence of underground structures such as ore bodies or petroleum reservoirs.
Magnetic Methods
Magnetic methods rely on detecting variations in the Earth’s magnetic field caused by magnetic minerals or geological structures. This technique is particularly useful in mapping geological formations and identifying mineral deposits.
Electrical Methods
Electrical methods involve measuring the electrical properties of the Earth’s subsurface, such as resistivity and conductivity. These methods are valuable for delineating groundwater resources, identifying mineral deposits, and assessing environmental contamination.
Earth’s Interior Layers
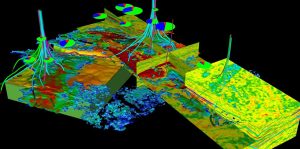
The Earth is composed of several distinct layers:
Crust
The Earth’s crust is the outermost layer, comprising solid rock that varies in thickness beneath the continents and oceans.
Mantle
Beneath the crust lies the mantle, a region of hot, semi-solid rock that extends to a depth of about 2,900 kilometers.
Outer Core
The outer core is a liquid layer composed mainly of iron and nickel. It surrounds the solid inner core and is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
Inner Core
The inner core is the Earth’s innermost layer, consisting of solid iron and nickel alloy under immense pressure.
Seismic Waves and Their Role
Seismic waves are vibrations that propagate through the Earth in response to geological events such as earthquakes or explosions. These waves provide valuable information about the Earth’s internal structure and composition.
Gravity plays a crucial role in geophysics by influencing the behavior of seismic waves and the distribution of mass within the Earth. Gravity anomalies can reveal subsurface geological features and help geophysicists interpret seismic data.
Magnetic Field and Geophysics
The Earth’s magnetic field results from the movement of molten iron in the outer core. Magnetic anomalies detected at the Earth’s surface provide insights into the geological composition and history of different regions.
Electrical Methods in Geophysics
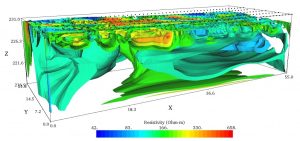
Electrical methods measure the conductivity and resistivity of subsurface materials to infer geological properties such as lithology, fluid content, and structural features.
Geophysics has diverse across various industries:
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Geophysical surveys are essential for locating underground reservoirs of oil and natural gas.
- Mineral Exploration: Geophysical techniques help identify mineral deposits and assess their economic potential.
- Environmental Studies: Geophysical methods are used to assess groundwater resources, monitor land subsidence, and detect pollution.
- Archaeology: Geophysical surveys can reveal buried archaeological features without excavation, aiding in cultural heritage preservation.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Deep Earth Exploration: Accessing deeper layers of the Earth remains a significant challenge due to technological limitations.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in instrumentation and data processing techniques is essential for advancing the field of geophysics.
Conclusion
Geophysics serves as a window into the Earth’s complex and dynamic interior. By employing various methods such as seismic, gravity, magnetic, and electrical surveys, scientists can unravel the mysteries of our planet’s structure and processes. As technology advances, the field of geophysics will continue to evolve, providing invaluable insights into Earth’s past, present, and future.
FAQs
What is the primary goal of geophysics?
Geophysics aims to understand the physical properties and processes of the Earth by studying its internal structure and dynamics.
How do seismic waves help in geophysical exploration?
Seismic waves provide information about subsurface structures, helping geophysicists map geological formations and identify potential resources.
What are some challenges in deep Earth exploration?
Accessing deeper layers of the Earth poses challenges due to technological limitations and extreme environmental conditions.
Why is geophysics important for environmental studies?
Geophysical methods are crucial for assessing groundwater resources, monitoring land subsidence, and detecting environmental pollution.
How does geophysics contribute to archaeology?
Geophysical surveys can reveal buried archaeological features without excavation, aiding in the preservation and study of cultural heritage.