In recent years, the field of rehabilitation therapy has witnessed a remarkable transformation, thanks to the integration of robotics. Robotics rehabilitation is revolutionizing the way patients recover from injuries, surgeries, and neurological disorders, offering new hope and improved outcomes. This article explores the significant advancements in robotics rehabilitation, the technology behind it, and its impact on patient care.
The Evolution of Rehabilitation Therapy
Traditionally, rehabilitation therapy has relied heavily on manual techniques and exercises guided by physical therapists. While effective, these methods have limitations, especially when dealing with complex cases or patients with severe impairments. The introduction of robotics into rehabilitation therapy has addressed many of these challenges, providing more precise, consistent, and personalized treatment options.
The Technology Behind Robotics Rehabilitation
Robotics rehabilitation encompasses a wide range of technologies designed to assist and enhance the recovery process. Some of the key components include:
1. Robotic Exoskeletons
Robotic exoskeletons are wearable devices that provide support and assistance to patients with mobility impairments. These exoskeletons can be used for various purposes, including gait training, muscle strengthening, and improving balance. By mimicking natural movements, they help patients relearn walking patterns and regain their independence.
2. Robotic Arm and Hand Devices
For patients with upper limb impairments, robotic arm and hand devices offer targeted therapy. These devices use sensors and actuators to facilitate precise movements, enabling patients to perform tasks they might otherwise find challenging. This technology is particularly beneficial for stroke survivors and individuals with spinal cord injuries.
3. Robotic Gait Trainers
Robotic gait trainers are designed to assist patients in relearning how to walk. These devices use a combination of sensors, motors, and computer algorithms to provide real-time feedback and adjust the patient’s movements. This ensures that the therapy is tailored to the individual’s needs and progress.
4. Virtual Reality (VR) Integration
Virtual reality is increasingly being integrated into robotics rehabilitation. VR environments provide immersive and engaging experiences that motivate patients to participate actively in their therapy. By combining VR with robotic devices, therapists can create customized rehabilitation programs that simulate real-life scenarios.
The Benefits of Robotics Rehabilitation
The integration of robotics into rehabilitation therapy offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Enhanced Precision and Consistency
Robotic devices provide precise and consistent movements, reducing the risk of human error. This level of accuracy is particularly important in rehabilitation, where small deviations can impact the effectiveness of therapy.
2. Personalized Treatment Plans
Robotics rehabilitation allows for highly personalized treatment plans. The technology can be adjusted to meet the specific needs and goals of each patient, ensuring that therapy is tailored to their unique condition and progress.
3. Increased Motivation and Engagement
The use of robotics and VR in rehabilitation makes therapy more engaging and enjoyable for patients. This increased motivation can lead to better adherence to treatment plans and faster recovery times.
4. Objective Measurement and Feedback
Robotic devices provide objective measurements and real-time feedback on a patient’s performance. This data is invaluable for therapists, allowing them to track progress, make informed adjustments to treatment plans, and set achievable goals.
5. Reduced Physical Strain on Therapists
Manual therapy can be physically demanding for therapists, leading to fatigue and potential injuries. Robotics rehabilitation reduces the physical strain on therapists, enabling them to provide high-quality care without compromising their own well-being.
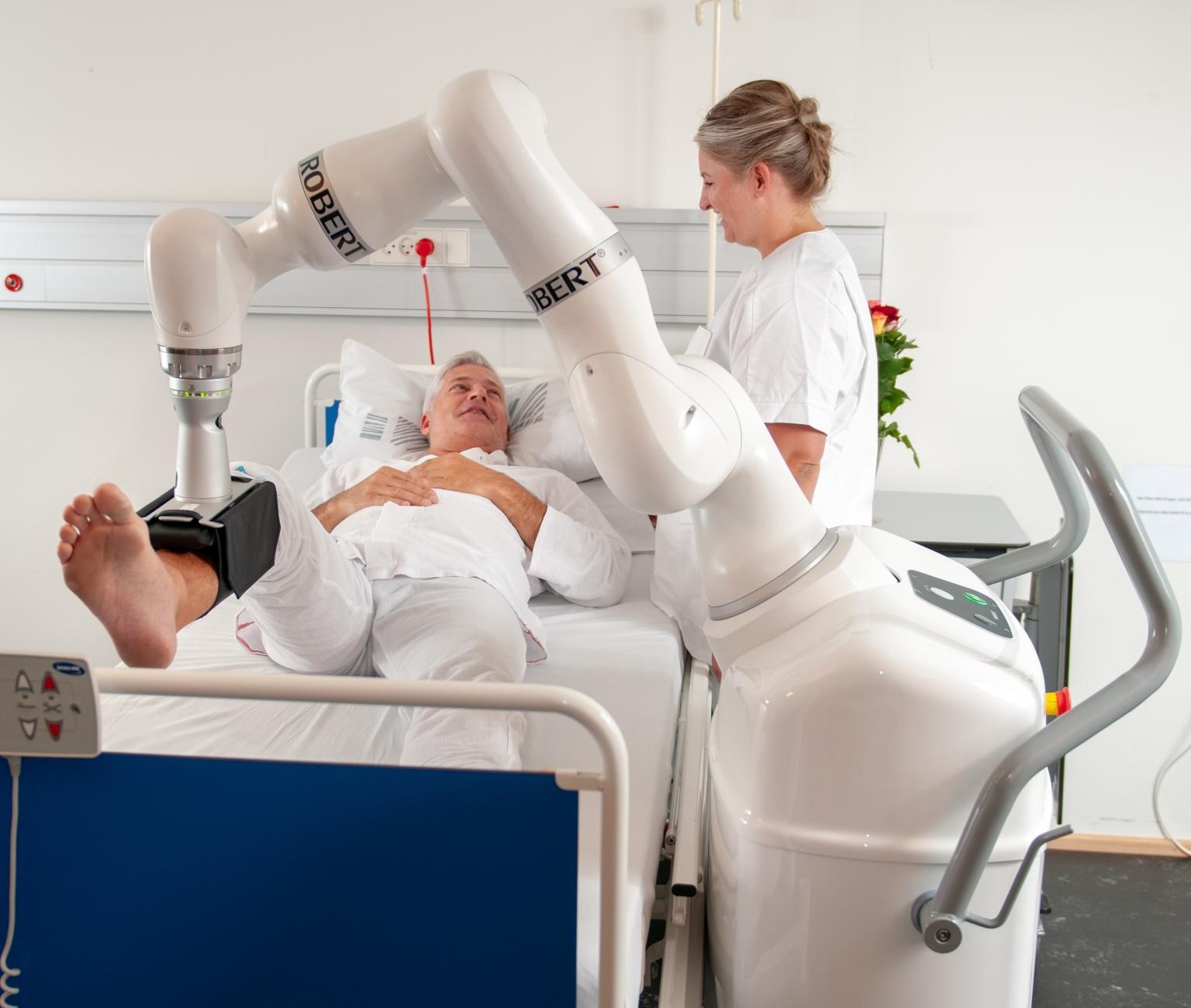
Applications of Robotics Rehabilitation
Robotics rehabilitation is being applied across a wide range of medical conditions and settings. Some of the notable applications include:
1. Stroke Rehabilitation
Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, and robotics rehabilitation has shown great promise in helping stroke survivors regain function. Robotic devices assist with repetitive movements, promoting neuroplasticity and facilitating the recovery of motor skills.
2. Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation
For individuals with spinal cord injuries, robotics rehabilitation offers new possibilities for regaining mobility and independence. Robotic exoskeletons and gait trainers help patients relearn walking patterns and improve muscle strength.
3. Orthopedic Rehabilitation
After orthopedic surgeries or injuries, robotics rehabilitation can accelerate the recovery process. Robotic devices provide controlled and precise movements, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster healing.
4. Pediatric Rehabilitation
Children with developmental disorders or injuries can benefit from robotics rehabilitation. The technology can be adapted to suit the needs of young patients, making therapy more engaging and effective.
5. Neurological Rehabilitation
For patients with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis, robotics rehabilitation offers targeted therapy to improve motor function and quality of life.
Challenges and Future Directions
While robotics rehabilitation holds immense potential, there are still challenges to overcome. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Cost and Accessibility
The cost of robotic devices can be prohibitive for some healthcare facilities and patients. Ensuring that these technologies are accessible to a wider population is a critical challenge that needs to be addressed.
2. Training and Integration
Healthcare providers need specialized training to effectively use robotic devices in rehabilitation therapy. Integrating these technologies into existing treatment protocols requires careful planning and coordination.
3. Ongoing Research and Development
Continued research and development are essential to further enhance the capabilities of robotics rehabilitation. Advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of this field.
Conclusion
Robotics rehabilitation is transforming the landscape of rehabilitation therapy, offering new hope and improved outcomes for patients with a wide range of conditions. The technology behind robotics rehabilitation provides enhanced precision, personalized treatment plans, and increased motivation for patients. While challenges remain, the future of robotics rehabilitation looks promising, with ongoing research and development paving the way for even more innovative solutions. As this field continues to evolve, it has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for countless individuals, helping them regain their independence and achieve their rehabilitation goals.