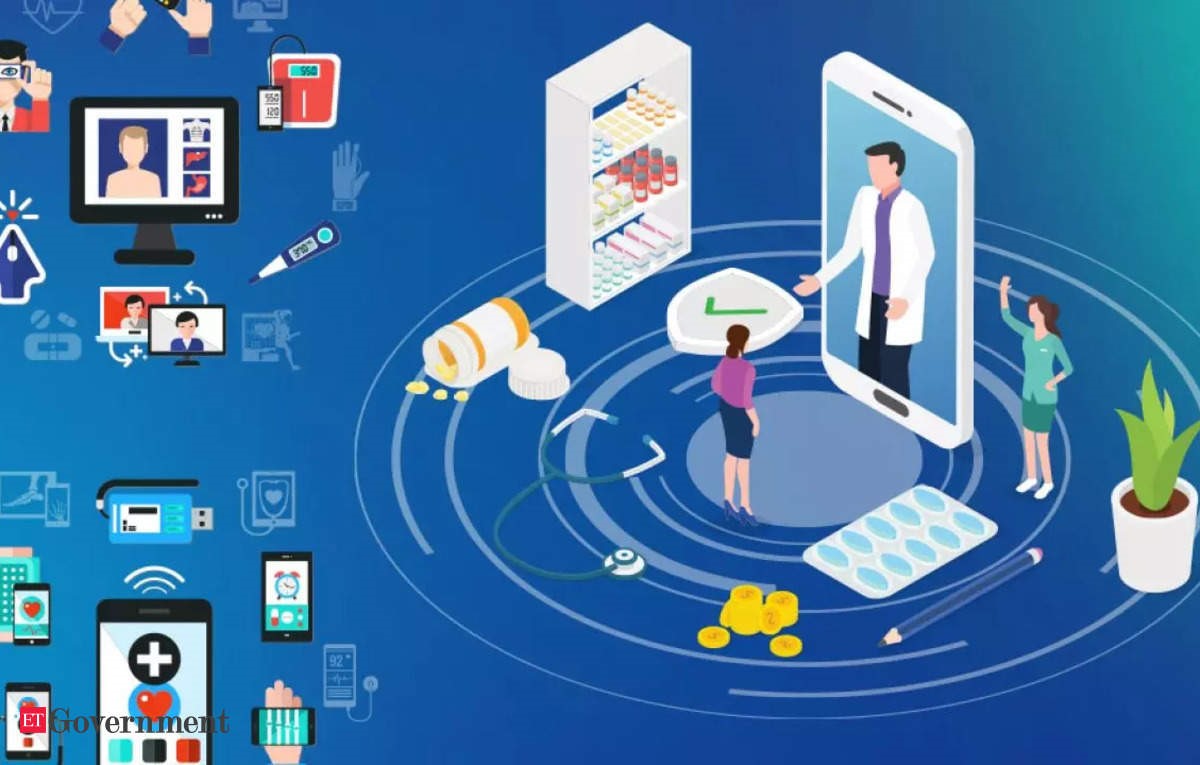
In recent years, the healthcare industry has witnessed a transformative shift, driven by the rapid advancement of technology. At the forefront of this evolution are AI-powered diagnostics and telemedicine, two domains that have synergistically combined to revolutionize patient care. As we delve into 2024, these innovations are not just enhancing the efficiency of healthcare delivery but are also making it more accessible, precise, and personalized.
The Rise of Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of delivering healthcare remotely through telecommunications technology, has been on the rise for over a decade. However, the COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating its adoption worldwide. The convenience of virtual consultations, coupled with the necessity of minimizing physical contact, made telemedicine an essential component of healthcare systems globally.
By 2024, telemedicine has evolved beyond basic video consultations. It now encompasses a comprehensive suite of services, including remote monitoring, digital therapeutics, and virtual health coaching. This evolution has been significantly bolstered by advancements in AI diagnostics, which have enhanced the accuracy and reliability of remote healthcare services.
AI Diagnostics: A Game Changer
AI diagnostics refers to the use of artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze medical data and assist in diagnosing conditions. These algorithms can process vast amounts of data with speed and precision, identifying patterns that may be imperceptible to human clinicians. In 2024, AI diagnostics are playing a crucial role in telemedicine by providing clinicians with powerful tools to make informed decisions remotely.
One of the most significant advantages of AI diagnostics is its ability to improve diagnostic accuracy. Machine learning models, trained on extensive datasets, can recognize subtle indicators of diseases, often outperforming traditional diagnostic methods. For instance, AI systems can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with remarkable accuracy, identifying anomalies that might be missed by the human eye.
Enhancing Remote Patient Monitoring
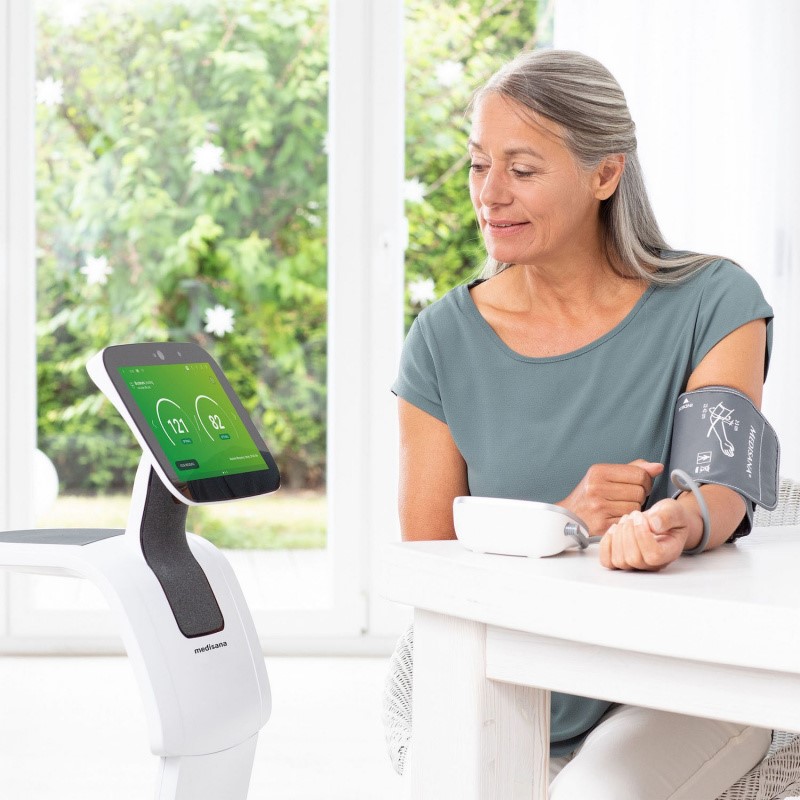
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a critical component of telemedicine, allowing healthcare providers to track patients’ health data in real-time. AI diagnostics have enhanced RPM by enabling continuous analysis of data from wearable devices and sensors. These devices can monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, transmitting data to healthcare providers for analysis.
AI algorithms can detect deviations from normal patterns, alerting clinicians to potential health issues before they become critical. For example, an AI-powered RPM system can identify early signs of a cardiac event, allowing for timely intervention and potentially saving lives. This proactive approach to healthcare is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions, where early detection and intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/63243907/GettyImages_1126452706.0.jpg)
Personalized Treatment Plans
The integration of AI diagnostics into telemedicine has also paved the way for personalized treatment plans. By analyzing individual patient data, AI systems can recommend tailored interventions that consider a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history. This level of personalization enhances the effectiveness of treatments and reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions.
In 2024, AI-driven personalized medicine is becoming a standard practice in telemedicine. For instance, AI algorithms can predict how a patient will respond to a particular medication, enabling clinicians to choose the most effective treatment with minimal side effects. This precision medicine approach is transforming the way chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions are managed remotely.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of AI-powered diagnostics in telemedicine are substantial, there are challenges and ethical considerations that need to be addressed. One of the primary concerns is data privacy and security. The vast amount of sensitive health data being transmitted and stored digitally necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect patient information from breaches.
Moreover, the reliance on AI algorithms raises questions about accountability and transparency. In cases where AI systems make diagnostic errors, determining liability can be complex. Ensuring that AI algorithms are transparent and explainable is crucial for maintaining trust in these technologies.
Another challenge is the potential for bias in AI diagnostics. If the data used to train AI models is not representative of diverse populations, it can lead to biased outcomes. Efforts must be made to ensure that AI systems are trained on diverse datasets and are regularly audited for bias.
The Future of AI-Powered Telemedicine
As we look to the future, the integration of AI diagnostics and telemedicine is poised to continue reshaping the healthcare landscape. The ongoing development of more sophisticated AI algorithms, coupled with advancements in telecommunications infrastructure, will further enhance the capabilities of telemedicine.
One area of potential growth is the use of AI in mental health diagnostics and treatment. AI-powered chatbots and virtual therapists are already being used to provide mental health support, and advancements in natural language processing are expected to make these tools even more effective.
Additionally, the expansion of 5G networks will improve the quality and speed of telemedicine services, enabling seamless high-definition video consultations and real-time data transmission. This will further bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare access, bringing quality medical care to underserved regions.
Conclusion
In 2024, AI-powered diagnostics are playing a pivotal role in enhancing telemedicine, making healthcare more accessible, accurate, and personalized. The combination of these technologies is not only transforming how healthcare is delivered but is also paving the way for a future where proactive and preventive care becomes the norm. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by these innovations, the ultimate goal remains clear: to improve patient outcomes and make quality healthcare accessible to all.