Introduction
The human cardiovascular system is a marvel of precision and complexity, and at its core lie four indispensable heart valves. These valves orchestrate the unidirectional flow of blood through the heart, meticulously opening and closing with each heartbeat. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of these valves, shedding light on their functions, potential disorders, associated symptoms, and available treatment options.

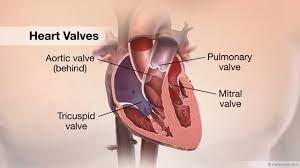
The Four Heart Valves
1. Tricuspid Valve
The tricuspid valve, aptly named for its three flaps or cusps, regulates the flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Anomalies such as tricuspid atresia, where individuals are born without this valve, or conditions like regurgitation and stenosis can impact its proper operation.
2. Pulmonic Valve
Responsible for managing the passage of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, the pulmonic valve plays a crucial role. Stenosis or regurgitation of this valve can develop over time, hindering its ability to function optimally.
3. Mitral Valve
Closing off the left atrium, the mitral valve facilitates the entry of oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left ventricle. Mitral valve prolapse, regurgitation, and stenosis are common issues associated with this valve, often arising from connective tissue disorders or heart-related events like a heart attack.
4. Aortic Valve
The final gatekeeper before oxygen-rich blood exits the heart to nourish the rest of the body, the aortic valve is of paramount importance. Aortic regurgitation or stenosis can compromise its efficiency, leading to potential complications.
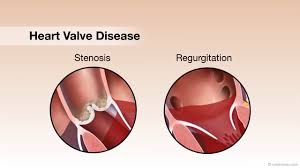
Linked Diseases and Conditions
Understanding heart valve problems involves recognizing two primary categories:
- Regurgitation: Occurs when a valve fails to close fully, resulting in blood flowing backward. This can be primary valvular (related to the valve) or secondary valvular (related to the heart’s chambers).
- Stenosis: Involves the thickening of valve tissue, restricting blood flow. Accumulation of calcium and deposits on the valve leaflets is a common cause. Over time, the heart thickens, posing a risk of severe illness or even death.
Symptoms of Heart Valve Problems
- Dizziness or Fainting
- Shortness of Breath
- Heart Palpitations (Irregular Heartbeat)
- Chest Pain
- Unexplained Swelling in the Body

Causes and Risk Factors
- Congenital Factors: Some individuals may be born with heart valve problems.
- Aging: The natural aging process can contribute to wear and tear on the heart valves.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes or other diseases, such as carcinoid disease, can increase the risk.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Certain disorders affecting connective tissues may damage heart valves.
- Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy habits like smoking can elevate the risk of heart valve issues.
- Secondary Valvular Problems: Enlargement of cardiac chambers or ventricles can lead to valve-related complications.
- Calcium and Deposits: Accumulation of calcium and deposits on valve leaflets can result in stenosis.
- Heart Attack: Events like heart attacks can damage the heart valves.
- Untreated Valve Issues: Ignoring or not treating valve problems promptly can escalate the risk of complications.
- Environmental Factors: Exposures to environmental toxins may contribute to valve damage over time.
Treatment Options
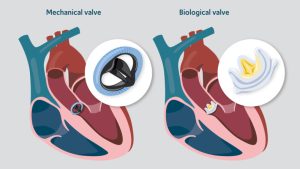
- Surgical Intervention
- Repairing Faulty Valves
- Valve Replacement
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Addressing Underlying Conditions
- Medication
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Comprehensive Treatment Plans
- Tailored Approaches
- Collaborative Care
- Monitoring and Follow-up
- Regular Check-ups
- Lifestyle Guidance
- Patient Education
- Empowering Patients
- Informed Decision-Making
Conclusion
A profound understanding of heart valves is imperative for safeguarding cardiovascular health. Malfunctions in these intricate mechanisms can exert additional strain on the heart, heightening the risk of various cardiovascular conditions and complications. Swift consultation with healthcare professionals, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment plans are essential for mitigating these risks. For those experiencing symptoms or suspecting heart valve issues, seeking prompt medical attention is paramount to ensure a comprehensive and effective approach to managing these concerns.