In today’s health-conscious era, understanding the correlation between diet and inflammation stands as a crucial element in optimizing overall wellness. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted relationship between what we eat and the body’s inflammatory responses, shedding light on how dietary choices significantly impact our health.
Understanding Inflammation
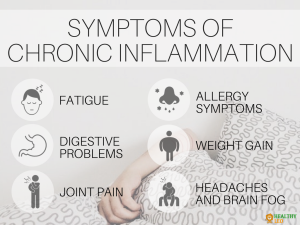
At its core, inflammation represents the body’s natural defense mechanism in response to injury, infection, or toxins. It exists in two forms: acute, a short-term response aiding healing, and chronic, a prolonged state linked to various diseases, including cardiovascular issues and autoimmune disorders.
Dietary Factors Influencing Inflammation
Our dietary habits hold immense power in modulating inflammation. Foods high in processed sugars, refined carbs, trans fats, and certain oils can exacerbate inflammation. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, fatty fish, and specific spices possesses anti-inflammatory properties, potentially mitigating chronic inflammation.
Macronutrients and Their Role in Inflammation
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins significantly influence inflammatory responses. The distinction between simple and complex carbohydrates, the impact of various fats (saturated, unsaturated, omega-3, and omega-6), and the relationship between different protein sources and inflammation are crucial considerations in crafting an anti-inflammatory diet.
Gut Health: A Key Player in Inflammation
The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in regulating inflammation. Dietary fibers, prebiotics, and probiotics serve as critical components in maintaining a healthy gut environment, thereby reducing inflammation and supporting overall health.
Impact of Specific Diets on Inflammation
The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its emphasis on whole foods, healthy fats, and fresh produce, showcases notable anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, other diets like DASH and Anti-Inflammatory Diets offer strategies to manage inflammation through dietary adjustments.
Lifestyle Factors and Inflammation
Beyond diet, lifestyle factors such as stress, sleep quality, and physical activity significantly influence inflammation. Stress management, adequate sleep, and regular exercise are pivotal in controlling chronic inflammation.

Conclusion
The intricate relationship between diet and inflammation underscores the profound impact of our food choices on overall health. By prioritizing an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins, while also considering lifestyle factors, individuals can potentially manage chronic inflammation and cultivate a healthier life.










