
This article is designed for PC enthusiasts, gamers, and tech-savvy individuals who are interested in understanding the significance of Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs) on motherboards. Readers seeking to enhance their knowledge about motherboard components and their impact on system stability and performance will benefit from this comprehensive guide.
Introduction: Unveiling the Power of VRM on a Motherboard
When building a PC, enthusiasts often focus on components like CPUs, GPUs, and RAM, but there’s a critical player that works behind the scenes to ensure stable performance—Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs). These electronic circuits, commonly referred to as buck converters, play a crucial role in regulating voltages to match the specific requirements of various components, including CPUs and memory. In this article, we delve into the world of VRMs, uncovering their significance, how they function, the essential components they comprise, and how to identify top-quality VRM configurations.
How VRM Works: The Engine Behind Stable Power Delivery
At its core, a VRM is akin to a specialized power supply that takes incoming voltages and converts them to levels suitable for different PC components. It acts as a secondary level of voltage regulation, ensuring that CPUs and other power-hungry parts receive consistent and clean voltage. VRMs transform the incoming 12V from EPS connectors into the optimal operating voltage range for modern CPUs. This function is crucial in maintaining stability and preventing absurd voltage surges or drops. VRMs also enable multiple generations of CPUs to function optimally on compatible motherboards, facilitating dynamic core voltage adjustments.

Components of VRM: Building Blocks of Stable Performance
Behind every VRM’s operation are several key components that work in harmony. MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are insulated gates that amplify or attenuate electronic signals, controlling the flow of current to the CPU. Chokes, cubic-shaped inductors, transform high-frequency AC signals into lower frequencies or direct currents, refining power delivery. Capacitors store and discharge energy to prevent voltage spikes, and PWM (pulse width modulation) controllers generate and adjust PWM pulses to regulate power delivery. These components come together to ensure consistent, clean power distribution, contributing to stable system performance.
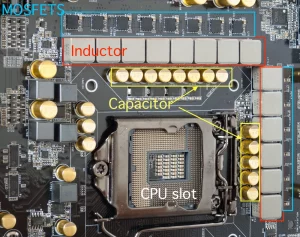
Decoding VRM Quality: Identifying Top-Tier Configurations
Distinguishing between a well-engineered VRM and a subpar one is crucial for system stability. A higher number of phases is a hallmark of a quality VRM configuration, as it divides the load into separate power stages, reducing stress and heat generation. Components like leak-resistant solid-state capacitors and premium alloy chokes are indicators of a high-quality VRM. These components resist aging, consume less power, and offer superior reliability. By understanding these quality indicators, users can make informed decisions when selecting motherboards and ensure their systems are equipped with robust VRMs.

Conclusion: The Unsung Champion of Motherboard Stability
While VRMs may remain in the background, their impact on system stability and performance is undeniable. These unsung heroes ensure that your PC’s components receive the clean and consistent power they need to function optimally. Through a deeper understanding of VRMs, enthusiasts can appreciate their role in achieving stable power delivery, preventing system crashes, and supporting optimal CPU performance. As users continue to explore the realms of PC building and optimization, the importance of VRMs as a backbone for efficiency and reliability becomes clearer than ever. So, whether you’re a gamer, a content creator, or a general user, remember that behind the scenes, VRMs are working tirelessly to keep your system running smoothly.










