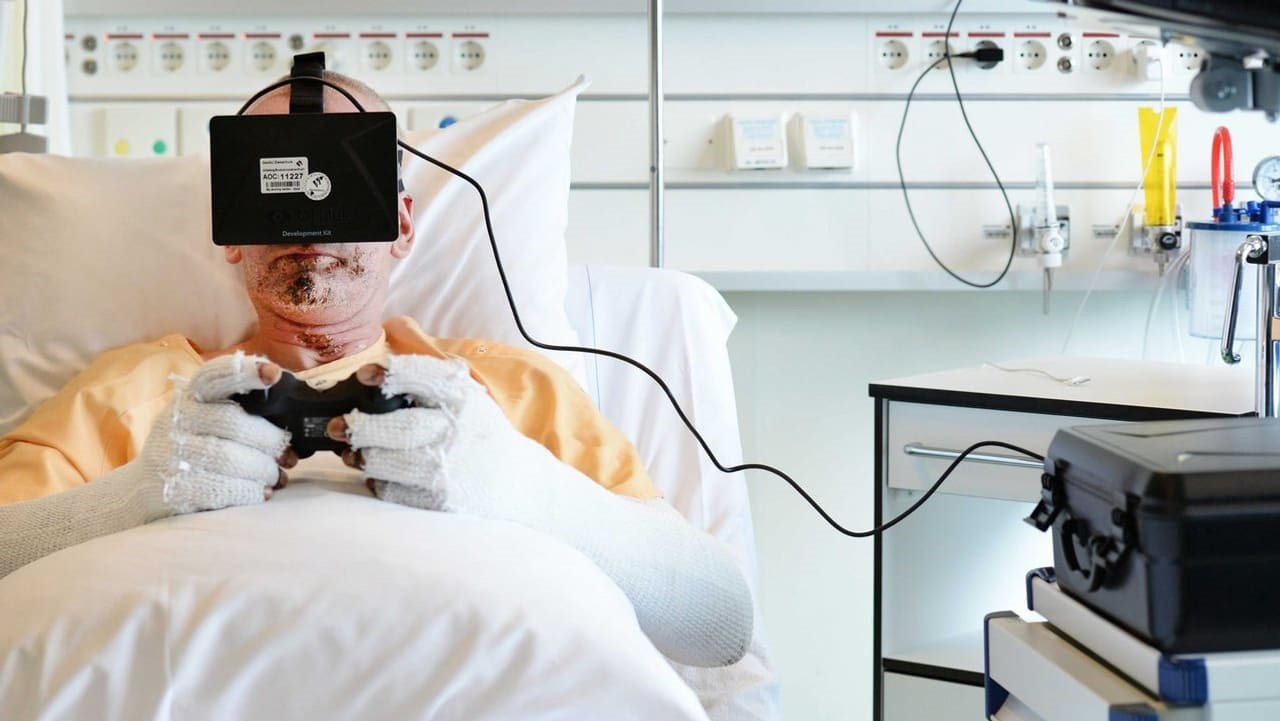
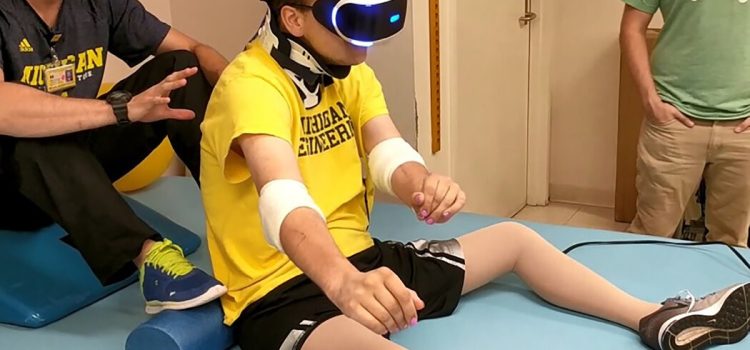
In a world where technology is evolving at a breakneck pace, the intersection of innovation and empathy is creating profound changes in the way we approach healthcare. One of the most promising advancements in recent years is the use of Virtual Reality (VR) in pain management. This technology, once primarily associated with gaming and entertainment, is now offering a new dimension of hope and healing for those grappling with chronic pain.
Understanding Pain and the Need for Change
Pain, both acute and chronic, is a complex and multifaceted experience that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be debilitating, affecting every aspect of a person’s life, from their physical abilities to their emotional well-being. Traditional pain management techniques, such as medication and physical therapy, often fall short, leaving many individuals in a relentless cycle of discomfort and despair.
The opioid crisis has further underscored the urgent need for alternative pain management strategies. Over-reliance on prescription painkillers has led to widespread addiction and devastating consequences for individuals and communities alike. In this context, the emergence of Virtual Reality as a tool for pain management is not just timely but essential.
Virtual Reality: A New Frontier in Pain Management
Virtual Reality offers a unique and immersive experience that can transport individuals away from their immediate reality. By donning a VR headset, users can find themselves in a tranquil forest, a serene beach, or even a whimsical fantasy world. This immersive distraction is not merely an escape but a powerful tool for reducing pain perception.
Studies have shown that VR can significantly decrease pain levels by engaging the brain in a way that traditional methods cannot. The immersive nature of VR captures the user’s attention, diverting it away from the pain signals that the brain is processing. This phenomenon, known as “distraction therapy,” is particularly effective because it taps into the brain’s ability to prioritize sensory inputs.
The Science Behind VR and Pain Relief
The efficacy of VR in pain management is rooted in neuroscience. When a person experiences pain, the brain is flooded with signals from the affected area. VR works by altering the user’s perception of these signals. By engaging multiple senses—sight, sound, and sometimes even touch—VR creates an alternate reality that competes with the pain signals for the brain’s attention.
Research has shown that VR can lead to a reduction in pain intensity, sometimes by as much as 50%. This is particularly beneficial for patients undergoing painful medical procedures or those dealing with chronic conditions such as fibromyalgia or arthritis. Moreover, VR has been found to be effective in reducing anxiety and stress, which often accompany chronic pain.
Empathy in Virtual Reality: A Personalized Approach
One of the most compelling aspects of using Virtual Reality in pain management is its potential for personalization. Unlike one-size-fits-all solutions, VR experiences can be tailored to the individual’s preferences and needs. This personalized approach is not only more effective but also more empathetic.
For instance, a patient who finds solace in nature can be transported to a lush, calming forest, complete with the sounds of rustling leaves and chirping birds. Another individual might find comfort in a guided meditation session set in a serene Zen garden. By catering to personal preferences, VR not only alleviates pain but also provides an emotional refuge.
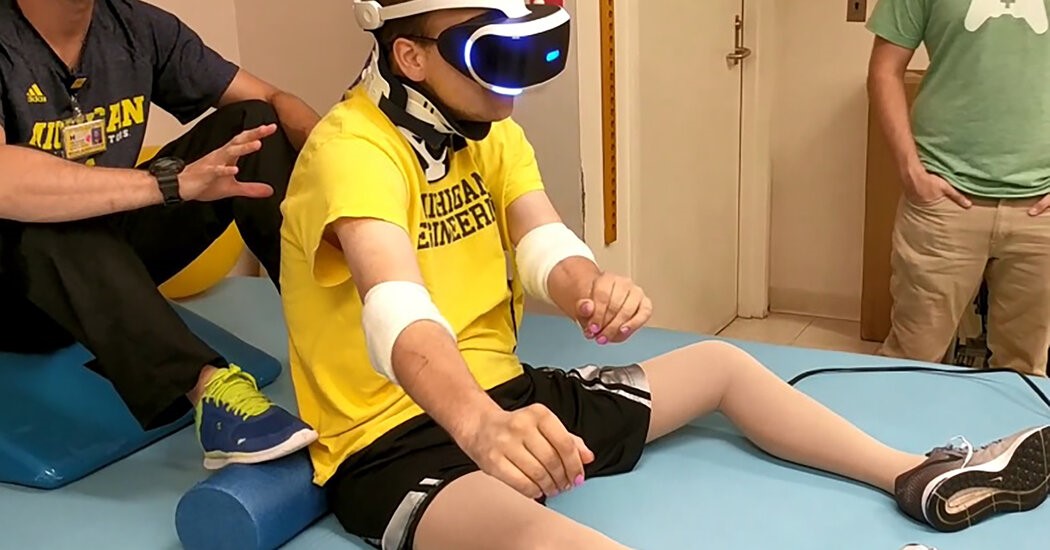
Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
The use of Virtual Reality in pain management is not just theoretical; it is being applied in real-world settings with remarkable success. Hospitals and clinics around the world are integrating VR into their pain management programs, offering patients an innovative and compassionate alternative.
For example, burn patients, who often endure excruciating pain during wound care, have reported significant pain reduction when using VR during treatment. Similarly, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy have found relief from both physical pain and the anxiety associated with their treatment through VR experiences.
One particularly touching story is that of a young girl named Emma, who was diagnosed with a rare form of bone cancer. The intense pain from her treatments made it difficult for her to find any semblance of normalcy. However, through the use of VR, Emma was able to escape to a world where she could swim with dolphins and explore underwater caves. This not only provided her with much-needed pain relief but also brought joy and excitement back into her life.
Challenges and the Path Forward
While the potential of Virtual Reality in pain management is immense, it is not without challenges. The cost of VR technology can be prohibitive, and there is a need for further research to fully understand its long-term effects and efficacy. Additionally, not all patients may be receptive to VR, and some may experience motion sickness or discomfort.
Despite these challenges, the future of VR in pain management is promising. As technology continues to advance, the cost of VR equipment is expected to decrease, making it more accessible to a wider range of patients. Moreover, ongoing research will likely yield new insights into optimizing VR experiences for pain relief.
Conclusion: A Compassionate Future
Incorporating Virtual Reality into pain management represents a compassionate and forward-thinking approach to healthcare. It acknowledges the complexity of pain and the need for innovative solutions that go beyond traditional methods. By offering an immersive escape and personalized experiences, VR not only addresses physical pain but also nurtures the emotional well-being of patients.
As we look to the future, the integration of empathy and technology in healthcare will continue to redefine what is possible. Virtual Reality is not just changing pain management techniques; it is transforming lives, offering hope, and reminding us of the power of human ingenuity and compassion. In a world where pain is often an inescapable reality, VR provides a glimpse into a world where healing and relief are within reach.