In the digital age, social media has become an integral part of daily life for millions around the globe. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok are not just avenues for social interaction but powerful tools that shape public perception and awareness on various issues, including mental health. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of social media on mental health awareness, exploring both the benefits and the drawbacks.
The Rise of Social Media and Mental Health Conversations
The advent of social media has democratized information dissemination, allowing individuals from diverse backgrounds to share their experiences and insights on mental health. Previously stigmatized and shrouded in secrecy, mental health issues are now more openly discussed, thanks to the visibility provided by social media platforms. This increased openness has led to several positive outcomes:
- Breaking the Stigma: Social media has played a crucial role in normalizing conversations about mental health. Hashtags like #MentalHealthAwareness, #EndTheStigma, and #YouAreNotAlone have created communities where individuals feel safe to share their struggles and seek support. Influencers and celebrities openly discussing their mental health challenges have further contributed to breaking down societal barriers.
- Educational Resources: Platforms like YouTube and Instagram host a plethora of educational content related to mental health. From expert advice to personal anecdotes, these resources provide valuable information to individuals seeking to understand mental health better. Accounts managed by psychologists, therapists, and mental health organizations offer practical tips and coping strategies, making mental health education more accessible than ever.
- Support Networks: Online communities and support groups have flourished on social media, providing a sense of belonging and support for individuals grappling with mental health issues. These virtual support systems can be particularly beneficial for those who may not have access to traditional forms of support, such as therapy or in-person support groups.
The Double-Edged Sword: Negative Impacts of Social Media on Mental Health
While social media has undoubtedly contributed to increased mental health awareness, it is not without its drawbacks. The very platforms that facilitate open conversations and support can also exacerbate mental health issues. Here are some of the negative impacts:
- Comparison and Self-Esteem: The curated nature of social media profiles often leads to unrealistic portrayals of life. Constant exposure to these idealized images can foster feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Studies have shown that excessive use of social media can lead to increased anxiety, depression, and body image issues, particularly among adolescents.
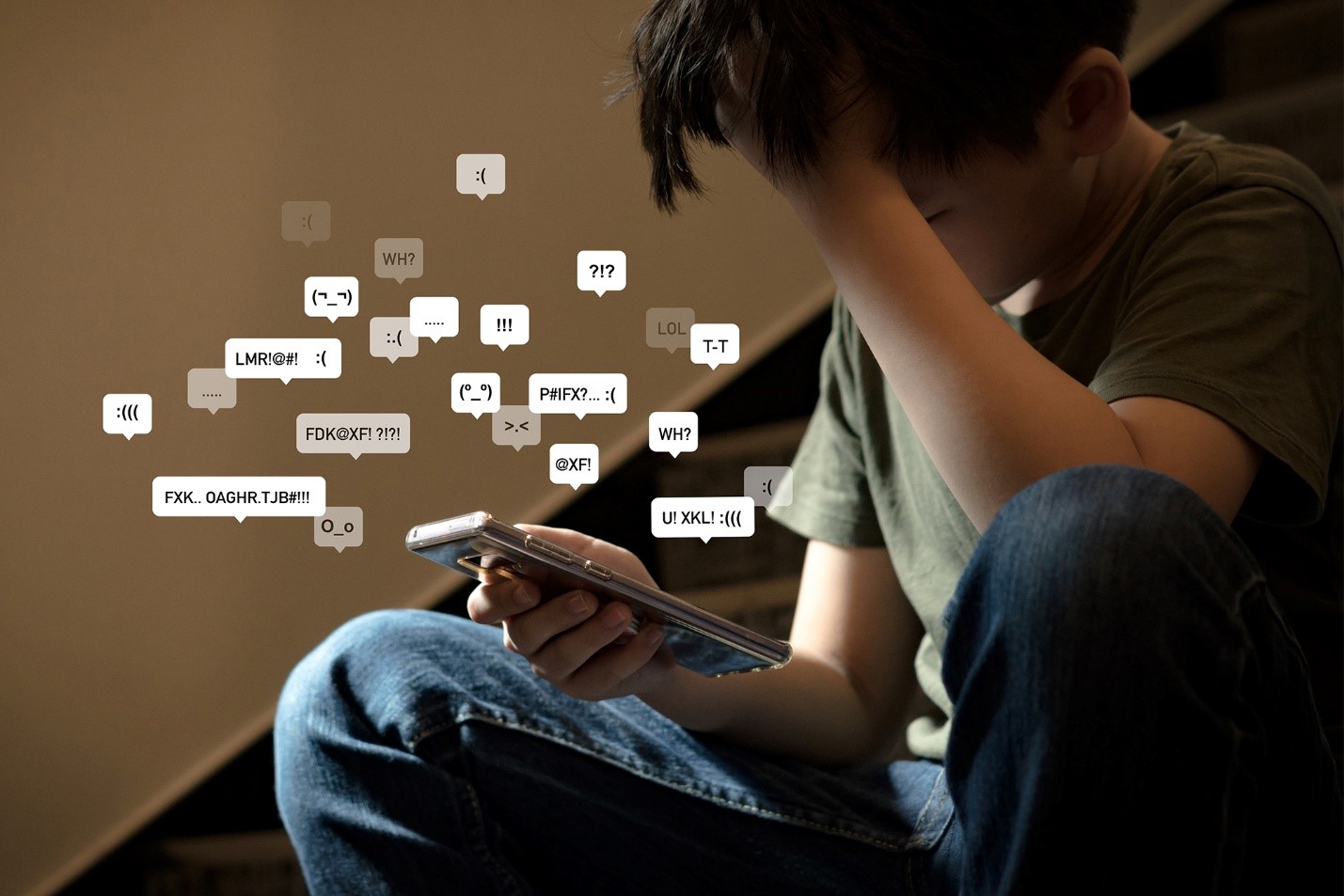
- Cyberbullying: The anonymity provided by social media can sometimes lead to negative behaviors such as cyberbullying. Victims of online harassment may experience severe emotional distress, leading to issues like anxiety, depression, and even suicidal thoughts. Cyberbullying is a significant concern that underscores the darker side of social media interactions.
- Information Overload: The sheer volume of information available on social media can be overwhelming. While some content is beneficial, there is also a proliferation of misinformation and unverified advice. This can lead to confusion and potentially harmful practices, especially when individuals turn to social media for mental health advice instead of consulting professionals.

Striking a Balance: Maximizing Benefits While Minimizing Harm
Given the dual nature of social media’s impact on mental health, it is essential to strike a balance to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential harm. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Digital Literacy: Educating users about the responsible use of social media is crucial. Digital literacy programs can teach individuals how to critically evaluate the content they encounter online, recognize misinformation, and understand the potential impact of social media on their mental health.
- Promoting Positive Content: Social media platforms and users alike can contribute to a healthier online environment by promoting positive and supportive content. Initiatives that encourage kindness, empathy, and constructive dialogue can help counteract the negative aspects of social media.
- Setting Boundaries: Encouraging users to set boundaries around their social media use can help mitigate its negative effects. This can include setting time limits, curating their feeds to include positive and supportive content, and taking regular breaks from social media to focus on offline activities and relationships.
- Access to Professional Help: While social media can be a valuable source of support and information, it should not replace professional mental health care. Encouraging individuals to seek help from qualified professionals when needed is essential. Platforms can also play a role by providing resources and information on how to access professional mental health services.
The Role of Social Media Companies
Social media companies have a significant role to play in shaping the impact of their platforms on mental health. By implementing policies and features that promote mental well-being, these companies can contribute to a healthier online environment. Some potential actions include:
- Algorithm Adjustments: Algorithms that prioritize positive and supportive content can help create a more uplifting online experience. Social media companies can also work to reduce the visibility of harmful content and misinformation related to mental health.
- Reporting and Support Features: Enhancing reporting mechanisms for cyberbullying and harassment, along with providing easy access to mental health resources, can help users navigate negative experiences on social media. Features that allow users to connect with mental health professionals directly from the platform can also be beneficial.
- Collaborations with Mental Health Organizations: Partnering with mental health organizations to develop and promote accurate and helpful content can enhance the quality of information available on social media. These collaborations can also lead to the development of innovative tools and features that support mental well-being.
Conclusion
Social media has undeniably transformed the landscape of mental health awareness, offering both opportunities and challenges. By fostering open conversations, providing educational resources, and creating support networks, social media has played a pivotal role in breaking down the stigma surrounding mental health. However, the negative impacts, such as comparison, cyberbullying, and information overload, highlight the need for a balanced approach.
Through digital literacy, positive content promotion, boundary setting, and access to professional help, individuals can navigate the complex relationship between social media and mental health more effectively. Social media companies also have a critical role in shaping the impact of their platforms, and their proactive involvement can contribute to a healthier online environment.
Ultimately, the goal is to harness the power of social media to enhance mental health awareness and support, while mitigating its potential harms. By working together, users, mental health professionals, and social media companies can create a more positive and supportive digital landscape for all.