Hepatitis is a viral infection that affects the liver, and can have serious health consequences if left untreated. Here’s how hepatitis impacts your liver health, and what you can do to protect your liver.
Types of Hepatitis
There are several types of hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Each type is caused by a different virus, and is transmitted differently. Hepatitis B and C are the most common types of hepatitis that can cause long-term liver damage.
Impact on Liver Health
When the hepatitis virus enters the liver, it can cause inflammation and damage to liver cells. Over time, this can lead to scarring of the liver, which is known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis can cause the liver to become hardened and less able to function properly, which can lead to serious health consequences.
In some cases, hepatitis B or C can lead to liver cancer, which can be life-threatening. The risk of liver cancer is higher in people with cirrhosis, as well as in people who have had hepatitis B or C for a long time.
Symptoms
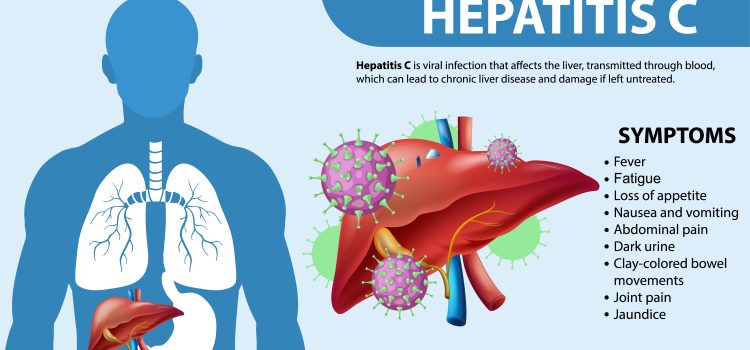
In the early stages of hepatitis, there may be no symptoms. However, as the infection progresses, symptoms may develop, including:
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation and testing.
Treatment
Treatment for hepatitis will depend on the type of hepatitis and the severity of the infection. In some cases, antiviral medications may be used to help control the virus and reduce inflammation in the liver. In other cases, close monitoring may be recommended to ensure that the virus does not cause any complications.
If cirrhosis has developed, treatment may focus on managing the symptoms and preventing further damage to the liver. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Prevention
Preventing hepatitis is key to protecting your liver health. Here are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of contracting hepatitis:
- Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B.
- Practice safe sex to reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis B or C.
- Avoid sharing needles or other injection equipment.
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly and avoiding contact with other people’s bodily fluids.
If you have hepatitis B or C, there are steps you can take to protect your liver health, including:
- Avoiding alcohol and drugs, as these can worsen liver damage.
- Eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise to support liver function.
- Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor liver function and detect any complications early.
In Conclusion
Hepatitis can have a significant impact on liver health, and can lead to serious complications if left untreated. It’s important to get tested for hepatitis if you are at risk, and to take steps to prevent transmission of the virus. If you have hepatitis, work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that’s right for you, and take steps to protect your liver health. With proper care and treatment, it’s possible to manage hepatitis and protect your liver from further damage.