This content is designed for individuals who are interested in understanding the distinctions between encryption, compression, and archiving in the context of data management. It caters to readers seeking clarity on these fundamental concepts in the digital landscape and how they contribute to data security, efficiency, and organization.
Demystifying Encryption, Compression, and Archiving
In the intricate realm of data management, three concepts play pivotal roles: encryption, compression, and archiving. While these terms are often intertwined, they each serve distinct purposes that contribute to the efficiency, security, and organization of digital data. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the differences between encryption, compression, and archiving, shedding light on their significance in the digital landscape.
Unveiling Encryption: Shielding Your Data
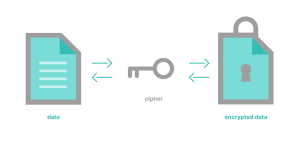
Encryption stands as a formidable fortress guarding sensitive information against prying eyes. This process involves transforming data into an unreadable format using complex mathematical algorithms. The primary objective of encryption is to render data unintelligible to unauthorized individuals. Only those equipped with the appropriate decryption key can unveil the encrypted data, ensuring confidentiality and privacy.
Encryption is a reversible process, setting it apart from techniques like hashing. Hashing transforms data into a fixed-length string, irreversibly altering its form. Symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods further shape this landscape. Symmetric encryption employs a single key for both encryption and decryption, while asymmetric encryption involves a pair of keys: public and private.
Encryption finds its stronghold in scenarios where data security is paramount. It safeguards data during transmission, secures sensitive information in storage, and shields personal, financial, corporate, and government data from unauthorized access.
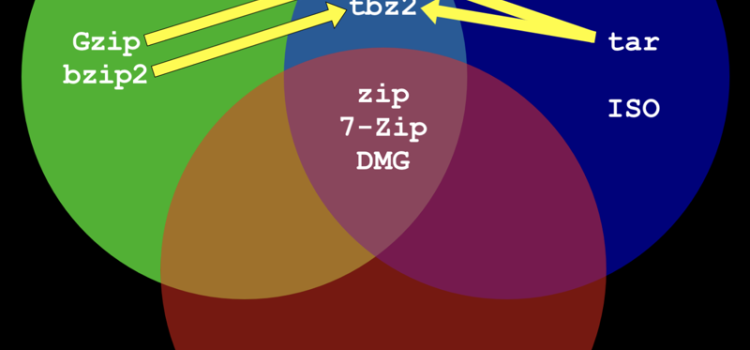
Compression: Efficiency Redefined
The realm of data management extends beyond security, delving into optimization. Compression emerges as a crucial strategy, maximizing resources by minimizing data size. This process not only aids efficient storage but also facilitates swifter data transmission.
Two primary compression techniques, lossless and lossy, dominate this landscape. Lossless compression retains all original data post-decompression, achieving size reduction by identifying and eliminating redundant patterns without sacrificing information. On the contrary, lossy compression balances compression ratio and data fidelity. It selectively discards less critical information, prioritizing efficient compression.
Compression finds its application in multimedia compression, file archiving, and database management, enhancing efficiency and reducing storage footprint.
Archiving: Beyond Storage, Towards Organization
Archiving steps onto the stage as a master organizer, consolidating files and directories into a single entity—an archive. This approach streamlines storage and management while preserving original content and structure.
Through specialized algorithms, archiving compresses data, saving storage capacity and enabling faster data transfer. The process involves identifying, selecting, preparing, moving, indexing, and monitoring archived data. Indexing facilitates efficient search and retrieval within the archive, while monitoring ensures its integrity and accessibility.
Various archive formats, such as ZIP, RAR, TAR, and 7z, cater to diverse needs. Archiving serves as a valuable tool for file backups, software distribution, and data preservation.

Conclusion
Encryption, compression, and archiving are distinct pillars in the realm of data management. Encryption safeguards data integrity, compression optimizes storage and transmission, and archiving offers efficient organization. Each concept plays a vital role in enhancing digital experiences, fortifying security, and streamlining data processes. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, a comprehensive understanding of these concepts equips individuals with the tools to navigate the dynamic world of data management with confidence and expertise.