Introduction
Artificial intelligence is reshaping how we interact with technology, and at the heart of this change are large language models (LLMs). Yet big models often demand massive computing power. Enter Microsoft’s Phi-2—a 2.7 billion-parameter small language model (SLM) that punches well above its weight. By combining high-quality “textbook” data, smart scaling, and safety filters, Phi-2 matches or outperforms models up to 25× larger on reasoning and understanding tasks. In this article, we’ll explore Microsoft’s Phi-2, uncover its innovations, review benchmark results, and show how it brings powerful AI to more devices and developers.
Background: The Phi Family of Small Language Models
Microsoft Research launched the Phi series to prove that smaller models can still deliver cutting-edge performance. The lineup began with Phi-1 (1.3 B parameters), which excelled at code generation tasks like HumanEval and MBPP. Building on that success, the team released Phi-1.5 (also 1.3 B but with refined data curation) for improved reasoning and comprehension. Now, Phi-2 doubles the parameter count to 2.7 B while leveraging lessons learned from its predecessors. This evolution demonstrates a clear path: smarter data and training can narrow the gap between small and massive LLMs microsoft.com.
Innovations That Power Phi-2
Phi-2’s standout performance stems from three key innovations:
- Textbook-Quality Data
Instead of scraping all available web text, researchers focused on high-value sources: academic papers, manuals, and other reliable content. This “curated curation” ensures the model learns clear, factual language rather than noise. - Synthetic Data Augmentation
To boost reasoning skills, Phi-2’s training set includes AI-generated synthetic texts. These cover hypothetical scenarios, common sense puzzles, and structured logic problems. The synthetic layer reinforces the model’s ability to solve multi-step tasks huggingface.co. - Scaled Knowledge Transfer
Phi-2 builds directly on Phi-1.5’s trained weights. By initializing from a proven small model and expanding its capacity, training converges faster and more reliably than starting from scratch.
Together, these strategies let Phi-2 achieve “state-of-the-art” results among base models under 13 B parameters microsoft.com.
Benchmark Performance
Phi-2 shines on a range of language-understanding and reasoning benchmarks:
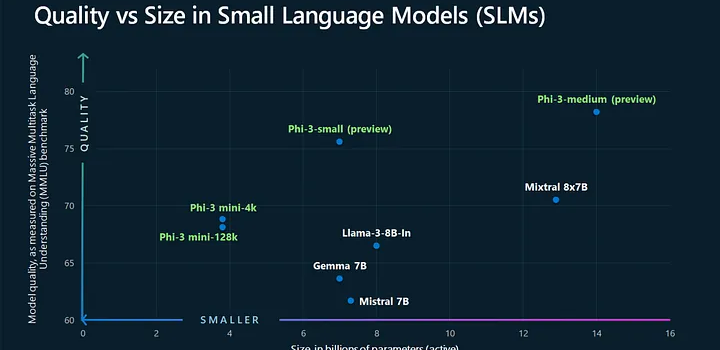
- Common Sense Reasoning: On tasks like the Winograd Schema Challenge, Phi-2 matches or beats 7 B–13 B models.
- Multi-Step Logical Tasks: In mathematics and code generation, Phi-2 rivals the performance of Llama-2-70B, a model nearly 25× larger.
- General Language Understanding: Phi-2 achieves near-top scores on GLUE benchmarks—tests that measure comprehension, sentiment analysis, and inference.
These wins show that careful data and scaling unlock more “bang for your buck” than simply adding parameters reddit.com.
Technical Specifications
Understanding the nuts and bolts of Phi-2 helps explain its flexibility:
- Architecture: Transformer with 2.7 B parameters; optimized layer normalization and attention mechanisms.
- Training Data: Over 1.4 trillion tokens combining high-quality web text, academic sources, and synthetic reasoning examples.
- Compute Efficiency: Designed for inference on modern GPUs and edge devices—no supercomputer required.
- Safety Measures: Filtered datasets remove disallowed content, and response moderation tools reduce harmful outputs.
- Open Source: Available under the MIT License, enabling developers to fine-tune or deploy Phi-2 in cloud or on-premises settings azure.microsoft.com.
Real-World Applications
Phi-2’s blend of power and portability makes it ideal for many use cases:
- On-Device Chatbots: Retail and service apps can embed Phi-2 to power customer support without sending data to remote servers.
- Education Tools: Tutors and learning platforms use Phi-2’s reasoning to explain concepts, generate practice problems, and grade essays.
- Code Assistance: Developers benefit from intelligent code completion and error-checking, all within IDEs on standard workstations.
- Research Summarization: Scientists use Phi-2 to condense academic papers into concise briefs, accelerating literature reviews.
- Content Moderation: With fine-tuning, Phi-2 detects policy violations or misinformation in user-generated text.
Because Phi-2 runs on lighter hardware, startups and small teams can leverage advanced AI features without huge infrastructure costs.
Deployment and Integration
Microsoft and partners have made it easy to get started with Phi-2:
- Azure AI Studio
Developers can spin up Phi-2 endpoints in minutes, paying only for usage. Prebuilt connectors simplify integration into websites and apps. - Hugging Face Model Hub
The microsoft/phi-2 repository offers code samples, fine-tuning scripts, and performance benchmarks. You can download the model weights and run it locally or in your own cloud environment huggingface.co. - NVIDIA NGC Catalog
Optimized containers let you deploy Phi-2 with TensorRT acceleration for maximum throughput on GPU clusters developer.nvidia.com.
Open-source licensing ensures you can modify Phi-2 for specialized domains—whether finance, healthcare, or legal—while keeping data private.
Future Outlook and Phi-Series Roadmap
Microsoft’s success with Phi-2 paves the way for next steps:
- Phi-3 and Beyond: Early reports hint at 4 B–6 B parameter variants that push reasoning further and support multimodal inputs (text + vision).
- Instruction Tuning: Turning Phi-2 into an interactive assistant via reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) can refine its conversational skills.
- Domain-Specific Models: Fine-tuning Phi-2 on medical, legal, or technical corpora will produce expert-level assistants.
- Energy Efficiency: Research continues on quantization and pruning techniques to run Phi models on mobile CPUs and even microcontrollers.
As Microsoft refines the Phi family, we can expect smaller, faster, and more capable AI models that bring intelligent features to every corner of technology.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s Phi-2 marks a breakthrough in language model AI—demonstrating that smaller, well-crafted models can rival giants of the field. By focusing on high-quality data, smart training methods, and open licensing, Phi-2 brings advanced reasoning and understanding to a wider audience. From on-device chatbots to educational apps and code assistants, Phi-2 lowers the barrier to deploying powerful AI. As the Phi series evolves, we’re entering a new age where “big” doesn’t always mean better. With Phi-2, smart engineering proves that efficiency and effectiveness can coexist, shaping the future of accessible AI for all.