
Introduction
Network troubleshooting commands are essential tools for network administrators to diagnose and resolve network issues efficiently. In this article, we will delve into seven crucial network troubleshooting commands that can help you identify and fix network problems quickly.
1. Ping: Testing Connectivity
Ping is a widely known network troubleshooting command available on various operating systems. It sends an ICMP echo request to a host and receives an ICMP echo reply if the host is reachable. By measuring the time it takes to reach the host and detecting errors or packet loss, ping provides insights into network connectivity.
To use the ping command, open the command prompt and enter ping followed by the IP address or URL. For instance:
ping www.facebook.com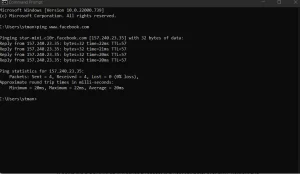
2. Tracert/Traceroute: Tracing the Route
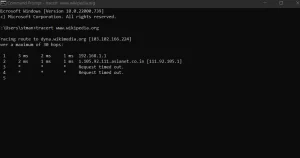
Tracert (or traceroute) reveals the route between a source and destination by displaying the IP addresses of routers along the path. By using ICMP routers, tracert helps pinpoint network bottlenecks and identify routing issues.
On Linux systems, use the terminal and type traceroute followed by the hostname or IP address. In Windows, use tracert followed by the hostname:
tracert www.wikipedia.com
3. Pathping: Combining Tracert and Ping
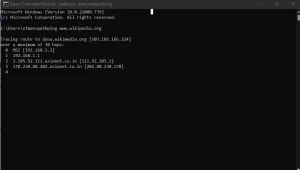
Pathping is a unique command developed by Microsoft, combining the functionality of tracert and ping. It identifies routers causing network issues and provides latency and packet loss data for each hop.
To use pathping, enter the command followed by the URL or IP address in the command prompt. You can customize parameters like maximum hops and timeout:
pathping -h 20 -w 200 www.example.com
4. Ipconfig (Windows) / Ifconfig (Linux): Network Configuration
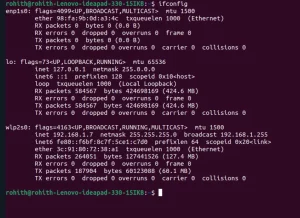
Ipconfig (Windows) and ifconfig (Linux) display TCP/IP network configurations. These commands show IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways bound to each adapter.
On Windows, open the command prompt and type ipconfig. On Linux, use the terminal and type ifconfig.
5. Nslookup: Diagnosing DNS Issues
Nslookup diagnoses DNS issues by looking up DNS records and their corresponding IP addresses. It’s useful for troubleshooting domain name resolution problems. To use nslookup, type the command followed by the domain name:
nslookup www.google.com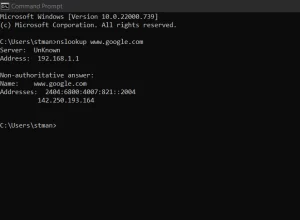
6. Netstat: Network Statistics
Netstat provides network statistics for your infrastructure, displaying network connections, routing tables, and network protocols used. This command is available on various systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and IBM OS.
To use netstat, open the command prompt or terminal and type netstat.
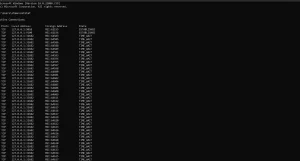
7. Route: Managing Routing Tables
The route command manages routing tables and is available on Windows, Linux, Unix-like systems, and more. It can clear routing tables, set network destinations, and configure IPv4 or IPv6 settings. In some Linux distros like Debian or Ubuntu, you might need to install it first:
sudo apt-get install net-tools
After installation, use the route command in the terminal or command prompt:
route -n
Conclusion
These seven network troubleshooting commands are valuable tools for network administrators. By mastering these commands, you can efficiently diagnose and fix network issues, ensuring smooth communication and connectivity across your network infrastructure.









